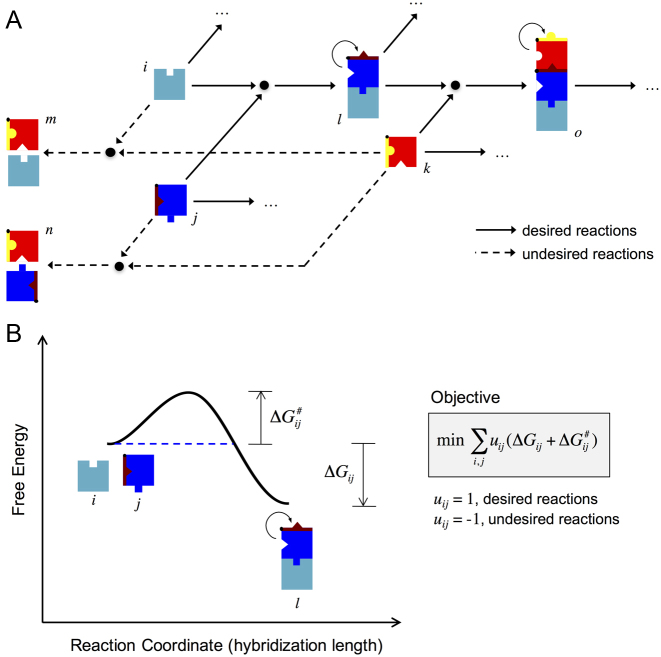
Figure 1.
(A) General scheme of an RNA hybridization network implemented with RNA-triggered riboregulators (i.e., riboregulators that allosterically switch from an OFF state to an ON state upon interaction with another riboregulator; colored boxes with notches). The arrows indicate the possible hybridization reactions; solid lines for desired interactions (energetically favorable) and dashed lines for undesired interactions (energetically unfavorable). (B) Energy landscape of a particular reaction within the network (between the molecules i and j). This shows the different conformational states and their free energy levels as a function of a reaction coordinate (number of intermolecular base pairs). A general objective function, which should be minimized, is shown. The terms ΔGij and ΔG#ij correspond to the free energies of hybridization and activation, respectively. Note that the free energy of hybridization is a negative magnitude, whereas the free energy of activation is a positive magnitude.