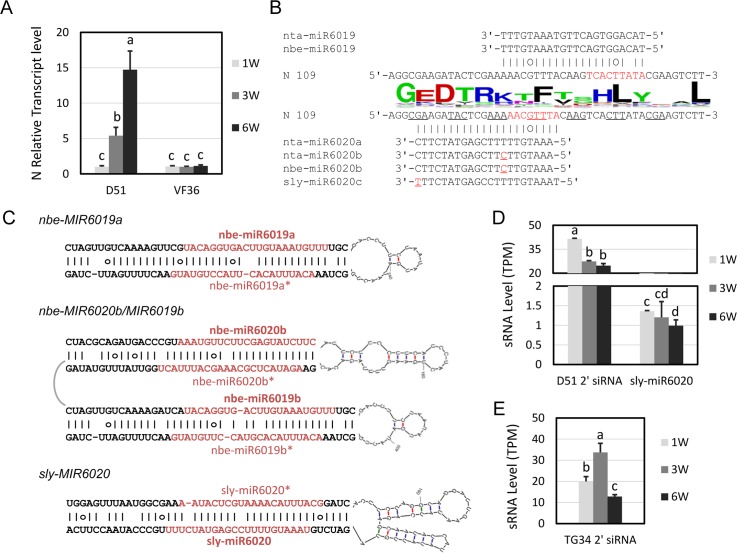
Fig 7. miR6019/6020 family is conserved in the Solanaceae plant family.
(A) Relative N transcript levels in tomato D51 (blue) and VF36 (red) plants at 1-, 3- and 6 WAG stages as determined by qRT-PCR. (B) Mature miR6019 and miR6020 sequences from different Solanaceae plants are paired to the TIR coding sequences of the N gene. The sequence logo of the TIR amino acid sequences encoded by the miR6019/6020 target sequence is shown. N sequences highlighted in red represent the binding sites for the miR6019 and miR6020 seed sequences. Polymorphic nucleotides in mature miR6020 are highlighted in red. (C) Secondary structures of the N. benthamiana and S. lycopersicum miR6019/6020 precursors. Mature miRNA and miR star are highlighted in red. (D) Levels of tomato miR6020 and secondary siRNAs derived from the coding region of N at 1-, 3- and 6 WAG stages. (E) Levels of tobacco secondary siRNAs derived from the coding region of N at 1-, 3- and 6 WAG stages. The data are the means of three replicates with SD. Different letters indicate significant differences between the treatments according to one-way ANOVA test (P < 0.05). The Y axes in A indicate relative fold. The Y axes in D and E are in TPM units.