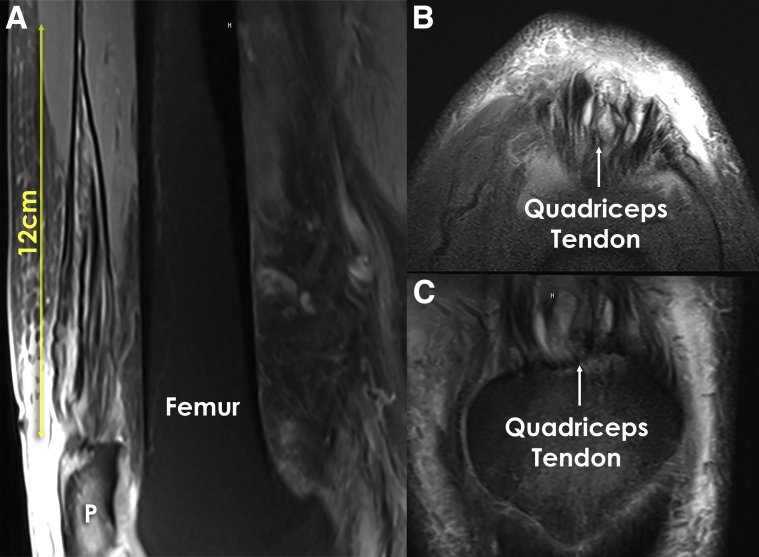
Fig 1.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the left knee showing quadriceps tendinopathy. (A) Sagittal view of the left knee showing tendinopathy. It is important to measure the length of the lesion to determine the length of the skin incision. (B) An axial view of the left knee showing changes in the quadriceps tendon. (C) Coronal view of the left quadriceps tendon attaching to the patella. The high signal changes consistent with tendinopathy can be seen. (P, patella.)