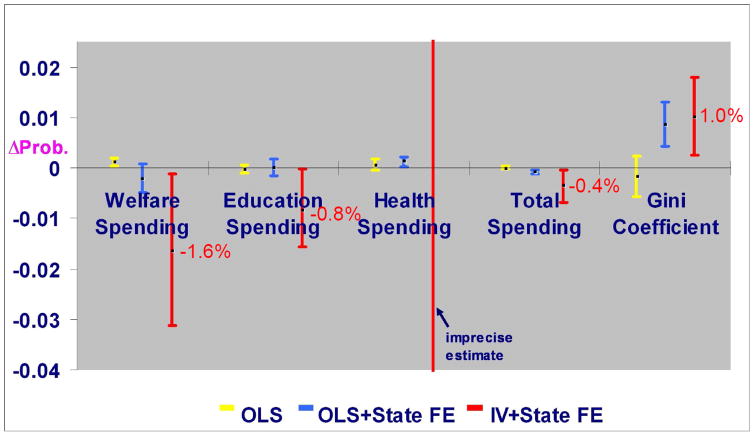
FIGURE 2. Effects of $250 per capita US state and local social spending and 0.1 unit Gini coefficient on individual probability (95% CI) of dying from coronary heart disease (431,637 adults aged 30–74 years).
OLS = ordinary least squares analysis; OLS + State FE = ordinary least squares analysis with state and time period fixed effects; IV + State FE = instrumental variable analysis with state and time period fixed effects. All models adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity, marital status, income, education, occupation, urban residence, and employment status; and state-level median household income, % with less than high school education, % Black, % urban, % aged 65 and older, unemployment rate, state governor party affiliation. All rank test P<0.10 except for healthcare spending (P=0.96). All endogeneity test P<0.05. Robust standard errors clustered by state and time period.