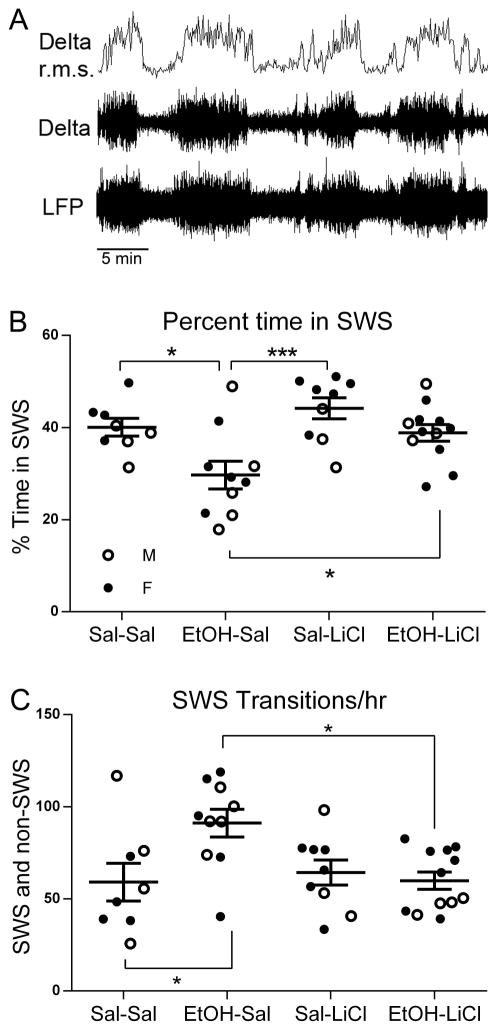
Figure 2.
A) Slow-wave sleep (SWS) was monitored with an electrode in the frontal cortex attached to a telemetry transmitter for wireless recording. Delta band r.m.s amplitude was extracted and used to quantify SWS bouts. B) The reduction in percent time in SWS in adults induced by P7 ethanol was prevented by co-treatment with LiCl (post-hoc Bonferroni tests, 6 total post-hoc comparisons). Mean % time in SWS +/− SEM is indicated on the y-axis. Males are represented by open circles and females by filled circles here and in C. C) The increase in SWS-waking transitions (sleep fragmentation) in adults induced by P7 ethanol was prevented by co-treatment with LiCl (post-hoc Bonferroni tests, 6 total post-hoc comparisons). Mean number of transitions from SWS +/− SEM is indicated on the y-axis. * = p < 0.05; ** = p < .01; *** = p < .001.