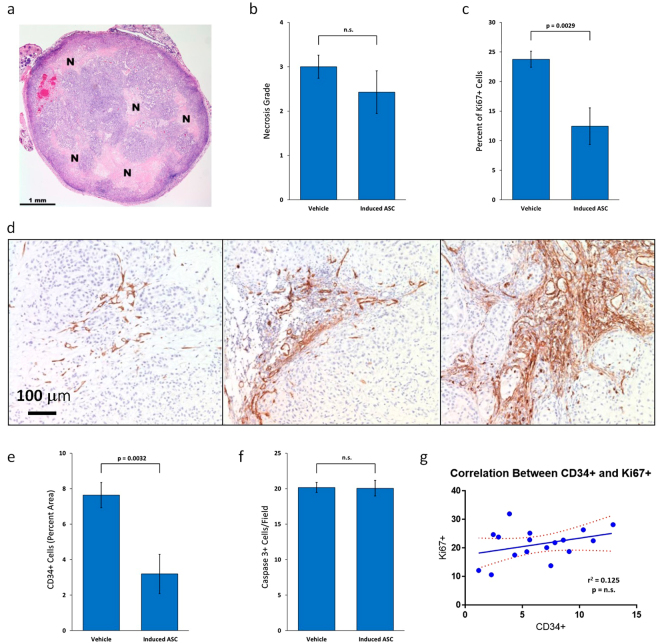
Figure 5.
TNF-α/IFN-γ-Induced Human Placental-Derived ASCs Inhibit Tumor Cell Proliferation and Vascularization in MDA-MB-231 Tumors in Nude Mice. (a) Representative section of H&E-stained MDA-MB-231 mammary fat pad tumor with grade 2 necrosis from mouse treated with TNF-α/IFN-γ-induced placental-derived ASCs. “N” marks areas of necrosis. (b) Mean necrosis grade in MDA-MB-231 mammary fat pad tumors from nude mice treated with either induced-ASCs or vehicle. (c) Mean percentage of proliferating cells in MDA-MB-231 mammary fat pad tumors from nude mice treated with either induced-ASCs or vehicle. (d) Representative sections of CD34 immunostained MDA-MB-231 mammary fat pad tumors showing different levels of vascularization all from different areas of tumors from mice treated with induced-ASCs. (e) Mean area occupied by blood vessels in MDA-MB-231 mammary fat pad tumors from nude mice treated with either induced-ASCs or vehicle. (f) Mean active caspase 3-expressing cells per field in MDA-MB-231 mammary fat pad tumors from nude mice treated with either induced-ASCs or vehicle. (g) Correlation between percent CD34+ stained area and percent Ki67+ cells in MDA-MB-231 mammary fat pad tumors in nude mice. n = 10. Error bars are SEM. P-values are based on a one-tailed student’s t-test.