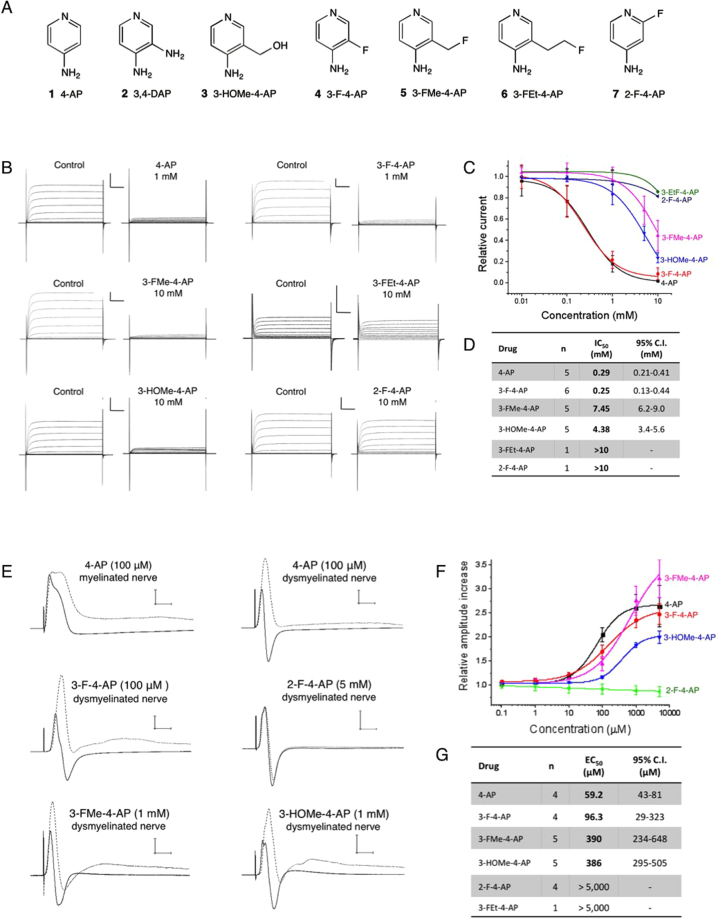
Figure 2.
Fluorinated derivatives of 4-AP. (A) Compounds tested in this study: (1) 4-aminopyridine. (2) 3,4-diaminopyridine. (3) 3-hydroxymethyl-4-aminopyridine. (4) 3-fluoro-4-aminopyridine. (5) 3-fluoromethyl-4-aminopyridine. (6) 3-fluoroethyl-4-aminopyridine. (7) 2-fluoro-4-aminopyridine. (B) Drug binding to K+ channels expressed in frog oocytes: K+ currents were generated by a series of 50 ms pulses from −70 mV to +40 mV in increments of 10 mV in the presence of cumulative concentrations of 4-AP derivatives. Each panel represents the K+ current recorded from the same oocyte before and after addition of each drug. Scale bar: 1 μA/10 ms. (C) Relative K+ current vs. concentration for each drug obtained at +20 mV. (D) Half-maximal inhibitory concentration of each molecule and 95% confidence interval obtained from fitting the data to the Hill equation. n = number of times each drug was tested in separate oocytes. (E) Drug binding to K+ channels in explanted mouse optic nerves: compound action potential (CAP) traces before (solid line) and after (dashed line) addition of each drug. Scale bar: 5 mV/5 ms. (F) Relative increase of maximum CAP amplitude vs. concentration for each drug. Amplitude was normalized to the amplitude before the drug. (G) Half-maximal effective concentration of each molecule and 95% confidence interval obtained from fitting the data to the Hill equation. n = number of times each drug was tested in separate nerves.