Figure 5.
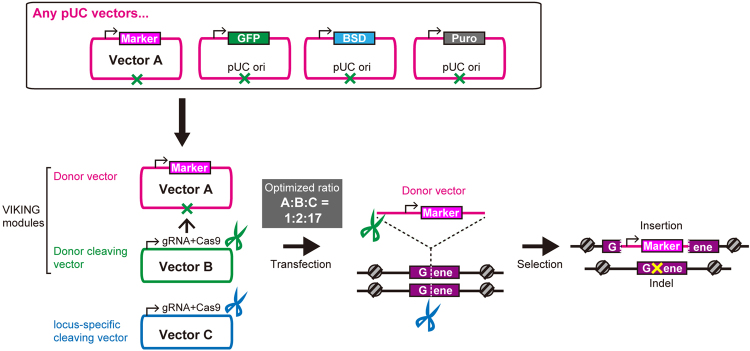
Schematic representation of non-homologous end joining (NHEJ)-based knock-in using versatile NHEJ-based knock-in modules for genome editing (VIKING). Step one: select the donor plasmid, which harbors the VIKING–gRNA1 sequence (Vector A). Any vector with a pUC backbone could be used as the donor vector without any customization from publicly available resources. Step two: construct the vector for cleaving the target genome (Vector C). Step three: simultaneously transfect the three vectors. Step 4: select cell lines harboring successful knock-in.