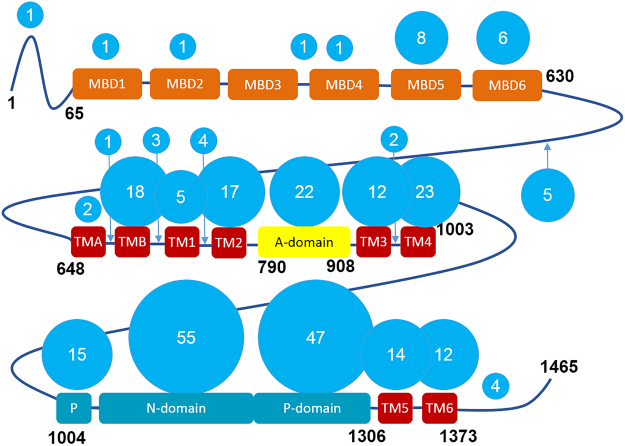
Figure 1.
Domain composition of ATP7B and the distribution of the Wilson disease mutations. ATP7B includes six cytosolic metal binding domains (MBD1-MBD6, orange), eight transmembrane helices (TMA-TM6, red), and the nucleotide-binding (N) and phosphorylation (P) domains (cyan), which together hydrolyze ATP, with the participation of the actuator (A) domain (yellow). The length of the interdomain linkers is not to scale. The number of known Wilson disease causing missense mutations in each domain and in the connecting loops, defined as distinct single amino acid substitutions, is shown in the blue circles. The list of mutations, as of 2010, was obtained from the Wilson disease mutation database (http://www.wilsondisease.med.ualberta.ca/database.asp)43. Except for the metal binding domains, a homology model of ATP7B5 based on the X-ray structure of the bacterial copper ATPase CopA2 was used to confirm domain assignment of the mutation sites.