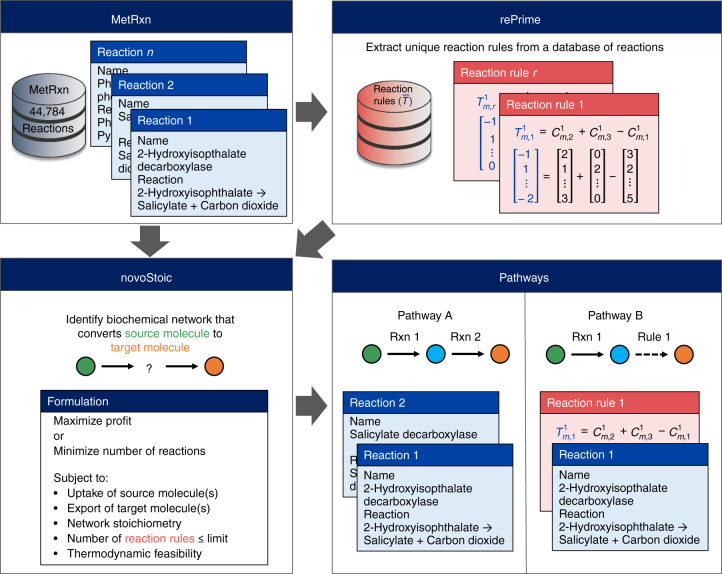
Fig. 1.
Schematic overview of the rePrime/novoStoic procedure. First, the rePrime procedure is used to pre-process the MetRxn database of reactions (blue boxes) to extract a unique set of reaction rules, Rλ (red boxes) at moiety size λ. The reaction rules are derived from the molecular signature of each participating metabolites and are captured by . The novoStoic procedure is then used to identify a series of intervening reactions and reaction rules that convert source molecule(s) (green circle) into target molecule(s) (orange circle) such that the profit can be maximized or the number of reactions in the pathway can be minimized. Other criteria including the number of reaction rules and thermodynamic feasibility of the pathway can be flexibly incorporated as constraints. By controlling the number of reaction rules, two possible pathways designed by novoStoic are shown in the bottom right panel. Pathway A uses two known reactions (blue boxes) that present in the MetRxn database, whereas pathway B uses a combination of a known reaction (blue box) and a reaction rule (red box) to perform the same conversion