Figure 1.
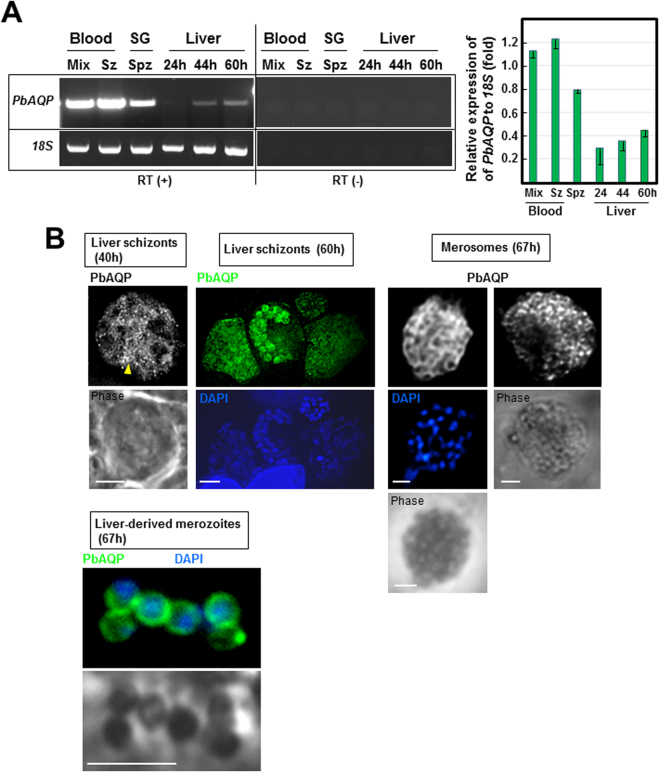
Expression of PbAQP during P. berghei developmental stages and localization of PbAQP in liver forms. (A) Transcriptional profiles of PbAQP in mixed blood forms, schizonts (Sz), salivary glands (SG) sporozoites (Spz) and liver forms at 24 h, 44 h and 60 h post-infection of Hepa1-6 cells assayed by RT-PCR. To verify the absence of genomic DNA contamination, RT-PCR reactions were set up without reverse transcriptase (RT) detecting no band (-). Two separate representative gels with cropped bands of PCR products for either PbAQP or 18S rRNA (loading control) are shown. The products of RT-PCR reactions with or without RT were run on the same gel but at different area to avoid contamination. The gel have been cut and the assembled products of RT-PCR with or without RT are separated by a vertical line. The 18S rRNA gene was used as a control to quantify PbAQP transcripts throughout the developmental stages of the parasite. Two separate agarose gels have been run for each transcripts The graph shows the quantitative analysis of PbAQP expression relative to 18S rRNA from 3 independent experiments. (B) Localization of PbAQP in intrahepatic P. berghei 40 h and 60 h p.i., merosomes and hepatic merozoites liberated from merosomes 67 h p.i. by IFA using anti-PbAQP antibodies. Arrowhead points to the tubular profiles. DAPI, blue. Bars, 10 μm.