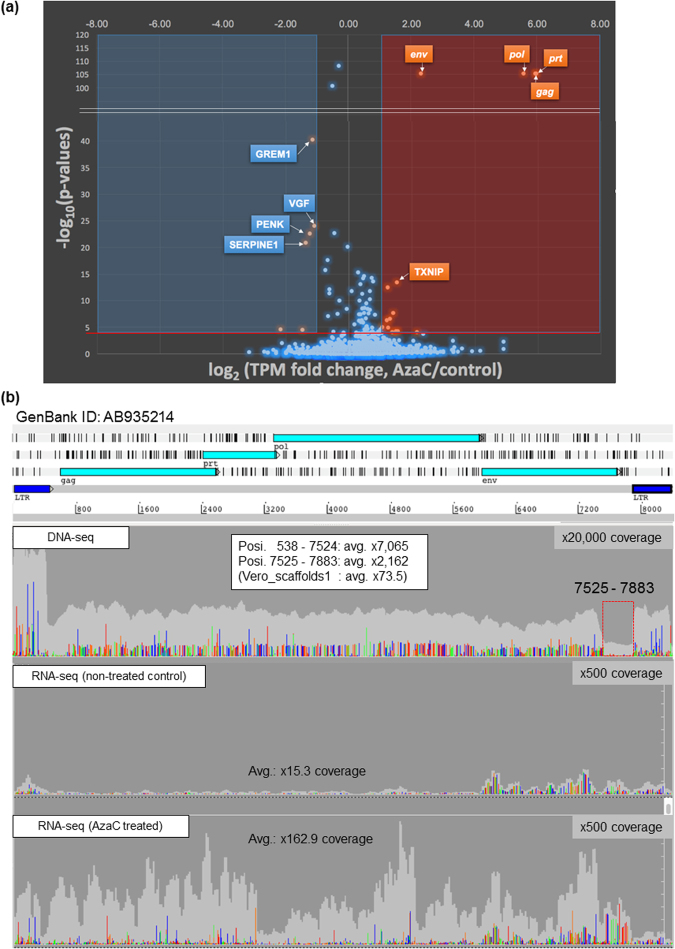
Figure 1.
Effects of the AzaC treatment on the transcriptome of Vero cells. The mRNA-enriched fractions obtained from AzaC-treated and -untreated Vero 0111 cells were subjected to whole-transcriptome sequencing as described in the Methods. (a) The transcriptome analysis was performed using CLC Genomics Workbench 10.1 software. Significant open-reading frames (ORFs) were considered to be those with a False Discovery Rate (FDR)-normalized p-value less than 0.0001, and visualized with a volcano plot. (b) Vero cells were cultured with (lower panel) or without (middle panel) AzaC. SRV-related short reads from all paired-end short reads were collected with 15 complete genome sequences of SRV as reference sequences as described in the Methods. The short reads obtained were assembled, extending at a 100% identity cut-off and gap-closing between contigs. A single reasonable contig (9.2 kb) was obtained, followed by gene assignment and an LTR finding analysis, which matches an 8367-bp full-size consensus SERV sequence identified in the genome of the Vero 0111 cell subline (GenBank: AB935214). All short reads obtained were remapped to the SERV of the Vero genome sequence (which is shown in the upper part of the panels), followed by the extraction of genetic variations, as described in the Methods. As a comparison, the SERV assembly collected from the DNA-seq analysis described in our previous study6 is also shown (upper panel). Read depth is shown in light gray, while the relative levels of SNVs mismatching with the consensus SERV sequence (AB935214) are shown in the following colors (A: light green, T: red, G: orange, C: dark blue).