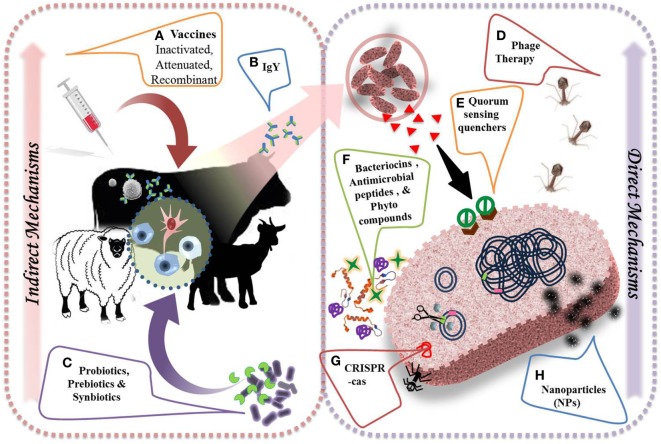
Figure 4.
Alternative strategies to combat antimicrobial resistance and their direct and indirect mechanisms of action. (A) Vaccination helps in preventing the course of infections by evolving immune cells (i.e. B cells  , T cells
, T cells  ) to develop an adaptive immunity by producing specific antibodies (
) to develop an adaptive immunity by producing specific antibodies ( ) against important pathogens. (B) Chicken egg yolk antibodies provide effective treatment approach against several viral and bacterial diseases. (C) Probiotics (
) against important pathogens. (B) Chicken egg yolk antibodies provide effective treatment approach against several viral and bacterial diseases. (C) Probiotics ( ), prebiotics (
), prebiotics ( ), and synbiotics improve general health by selectively stimulating innate immune cells (
), and synbiotics improve general health by selectively stimulating innate immune cells ( ). (D) Lytic bacteriophage or their purified gene products could be used to treat sepsis and few bacterial infections. (E) Quorum sensing quenchers (
). (D) Lytic bacteriophage or their purified gene products could be used to treat sepsis and few bacterial infections. (E) Quorum sensing quenchers ( ) could control virulence of pathogens by inhibiting the binding of auto-inducers (
) could control virulence of pathogens by inhibiting the binding of auto-inducers ( ) to respective receptors. (F) Antimicrobial peptides (
) to respective receptors. (F) Antimicrobial peptides ( ), bacteriocins (
), bacteriocins ( ), and phytocompounds (
), and phytocompounds ( ) directly inhibit the bacterial growth by acting on bacterial cell membrane. (G) Modified CRISPR-Cas approach targets resistance genes in pathogens and reverse the selective pressure of resistance. (H) Metal-based nanoparticles (
) directly inhibit the bacterial growth by acting on bacterial cell membrane. (G) Modified CRISPR-Cas approach targets resistance genes in pathogens and reverse the selective pressure of resistance. (H) Metal-based nanoparticles ( ) help in blockage of enzyme pathways, alteration of cell wall, and nucleic material pathways.
) help in blockage of enzyme pathways, alteration of cell wall, and nucleic material pathways.