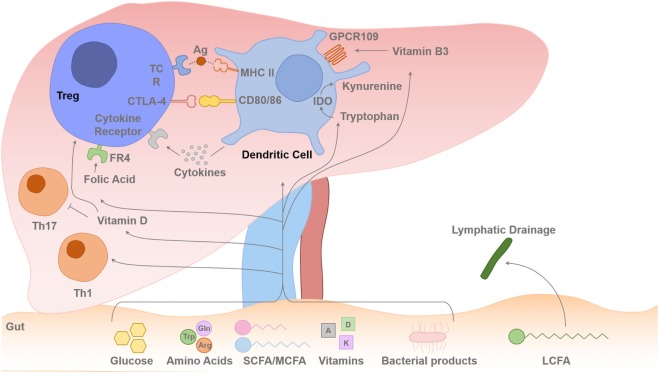
Figure 2.
Gut–liver axis and metabolites flux toward the liver. Intrahepatic T cell (including Treg cells) lineage fitness, function, survival, and proliferation are influenced by signals from the antigen presenting dendritic cells (DCs) and cytokines. The T cell receptor (TCR) binding to the foreign antigen–MHC II complex and co-stimulation provided by CD80 and CD86 binding to the T cells CD28/CTLA-4 induces T cell activation or inhibition of its function. Cytokines secreted by the DCs determine the differentiation pathway of the activated CD4 T cell to different Th1/Th2/Th17 lineages or Treg-cell survival with contact-dependent mechanism with DCs CD80/86. IL-2 is secreted in the liver by activated T effector cells, and this is required for Treg-cell survival and suppressive function. Dietary SCFAs (acetate, propionic acid, and butyrate) and MCFAs arrive to the liver via the portal vein, but LCFAs are absorbed via intestinal lymphatics and drain back into the systemic circulation via the thoracic duct. The amino acids, Glu and Arg, and glucose are also absorbed via the portal venous system towards the liver. There is always a certain degree of gut leakiness and bacterial product such as lipopolysaccharide reaches to the liver, and they rapidly undergo phagocytosis by hepatic sinusoidal Kupffer cells, which function as a sinusoidal firewall of the liver (32). The liver is enriched with fat-soluble vitamins such as vitamins A and D. DCs express immunosuppressive enzyme indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), which transform Trp into kynurenine, which is then metabolized into other catabolites through the action of enzymes within the kynurenine pathway (26, 33, 34). Trp-derived catabolites can mediate the tolerogenic effects of IDO by inducing apoptosis of activated but not resting T cells (35). Folic acid binds to folic acid receptor (FR4) on the Treg cell and Niacin (vitamin B3) interacts with GPCR109 on DCs. Glu, glutamine; Trp, tryptophan; Arg, arginine; SCFA, short-chain fatty acid; MCFA, median chain fatty acid; LCFA, long-chain fatty acid.