Figure 1.
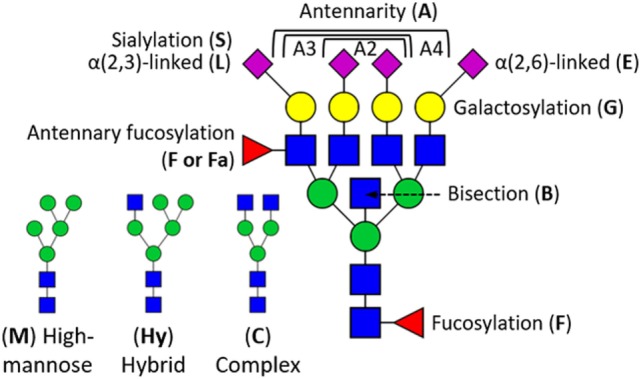
Schematic overview of glycosylation traits derived from human serum proteins. N-Glycan structures are generalized into high-mannose type (M), hybrid type (Hy), and complex type (C) by the number of mannoses (green circle) and antennary N-acetylglucosamines (blue square). High-mannose-type N-glycans can have up to nine mannoses, whereas each antennary N-acetylglucosamine can be terminally substituted with a galactose (yellow circle), and sialic acid (magenta diamond). Sialic acids (S) can either be α2,3-linked (L) or α2,6-linked (E). N-Glycans can further be modified with a fucose (F), optionally at an antennary N-acetylglucosamine (Fa), and structures may as well be bisected (B). In case of derived traits, the subject of the calculation is represented by the last letter, e.g., sialylation (S), and the group on which it is calculated by the preceding letters, e.g., triantennary fucosylated species (A3F). This, for instance, translates A3FGS into the sialylation per galactose within triantennary fucosylated species.
