Figure 2.
Glutamate Binding Pathways and Metastable Binding Sites
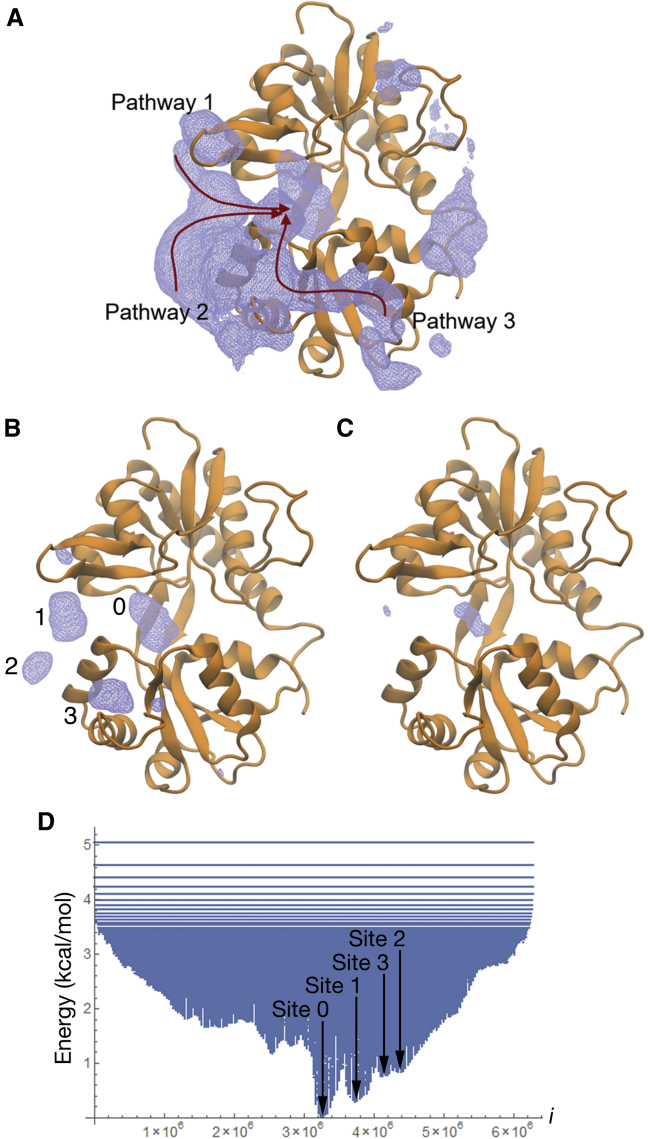
(A) The PMF calculated from the ligand density using a hard-sphere van der Waals approximation on a grid spacing of 0.5 Å along the x, y, and z axes contoured at 1.89 kcal mol–1. Data are from the monomeric LBD system with 10 ligands (Tmon2,3). The primary binding pathways for glutamate are depicted by arrows.
(B) The PMF, contoured at 1.16 kcal mol–1, defines the regions of metastable interaction, sites 0–3. Site 0 is the site of stable binding. Site 1 is shared by Pathways 1 and 2, site 2 is encountered in Pathway 2, and site 3 is encountered in Pathway 3. Site 1 spans the two lobes, involving R453 in Lobe 1 and E657, R660, and R661 in Lobe 2. Site 2 involves E657, R660, and R661 in Lobe 2. Site 3 involves R675 and R684 in Lobe 2. The residues involved in site 0 are shown in Figure 3A. Error analysis is provided in Figure S2.
(C) The PMF, contoured at 0.32 kcal mol–1, shows the global free energy minimum. This minimum overlaps well with the ligand density derived from crystal structures of the glutamate-bound complex (e.g., PDB: 1FTJ).
(D) The one-dimensional representation of the WT GluA2 ligand-binding PMF was obtained by first computing the three-dimensional PMF (A–C). Values of the three-dimensional PMF were indexed increasing in the z, y, then x directions, from (xmin, ymin, zmin), to produce the one-dimensional representation. The positions of sites 0–3 are indicated. Site 0 is the global free energy minimum and is set to 0 kcal/mol; sites 1–3 form local minima with free energies of 0.29, 0.83, and 0.75 kcal/mol, respectively.
See also Figures S2 and S8.