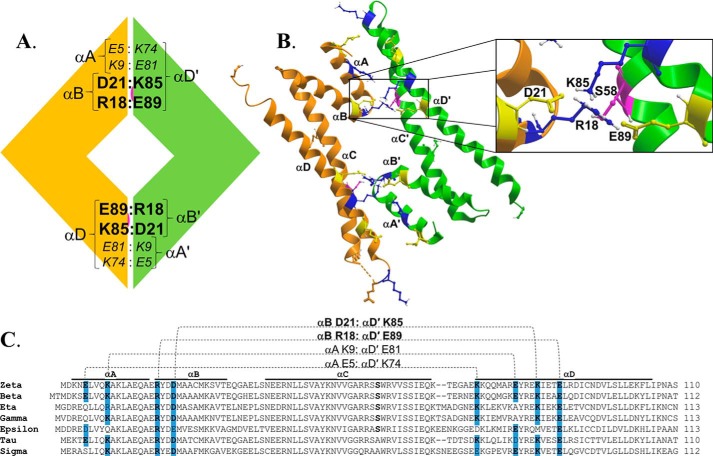
Figure 1.
Structural organization of the dimer interface in 14-3-3ζ. A, schematic representation of the predicted salt bridges at the dimer interface of 14-3-3ζ. The orange and green modules represent two monomer units of 14-3-3ζ, and residues shown in large boldface type represent predicted salt-bridging residues conserved across multiple 14-3-3 isoforms. The buried Ser58 phosphorylation site is also shown in pink. B, the dimer interface of 14-3-3ζ (residues 1–110) is shown in a ribbon representation with predicted key salt-bridging residues highlighted (acidic residues in yellow and basic residues in blue). The buried Ser58 phosphorylation site is shown in pink. The inset shows the dimer interface in greater detail with the predicted salt bridge residues labeled. C, an alignment of the N-terminal primary sequences encompassing the dimer interface of all seven isoforms of human 14-3-3 ζ, β, η, γ, ϵ, τ, and σ, with the predicted salt bridge residues highlighted and their proposed intermolecular interactions represented by dotted lines. The positions of the first four α-helices are indicated as αA, αB, αC, and αD.