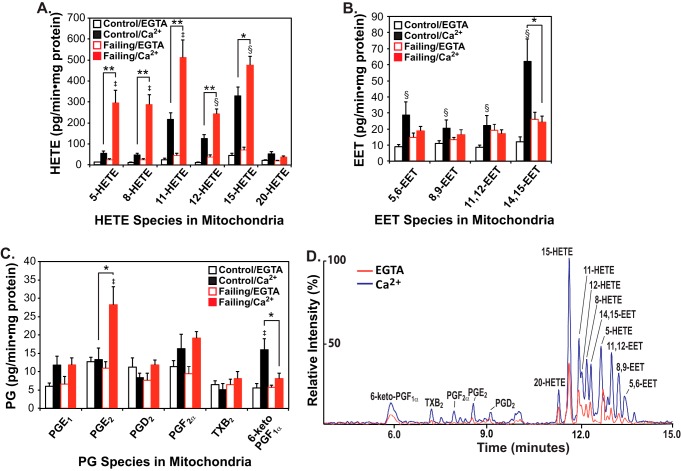
Figure 1.
Mass spectrometric analysis and quantitation of eicosanoids generated by non-failing and failing human heart mitochondria stimulated by calcium. Myocardial mitochondria were isolated from non-failing (control) and failing hearts by differential centrifugation as described under “Experimental procedures” and then sonicated in HEPES buffer (10 mm HEPES (pH 7.4) containing 10% glycerol and 1 mm DTT). Mitochondrial homogenates were incubated in the absence of Ca2+ (EGTA) or the presence of 200 μm free Ca2+ at 35 °C for 20 min. The reaction was stopped by addition of methanol (20% v/v final concentration) at 4 °C and diluted with water after addition of internal standards (250 pg each of TXB2-d4, PGE2-d4, and 12-HETE-d8). Eicosanoids were immediately isolated by solid-phase extraction, derivatized with AMPP, and analyzed by HRAM mass spectrometry. The resultant production of HETEs (A), EETs (B), and Prostaglandins (PGs) (C) is shown with the average ± S.E. (n = 6 for non-failing control hearts and n = 6 for failing hearts). *, p < 0.05, and **, p < 0.005 for control (non-failing) versus failing hearts. ‡, p < 0.005, and §, p < 0.05 for EGTA versus Ca2+. A representative LC-MS spectrum from non-failing control heart mitochondria in the absence (EGTA) or presence of Ca2+ is displayed in D.