Figure 2.
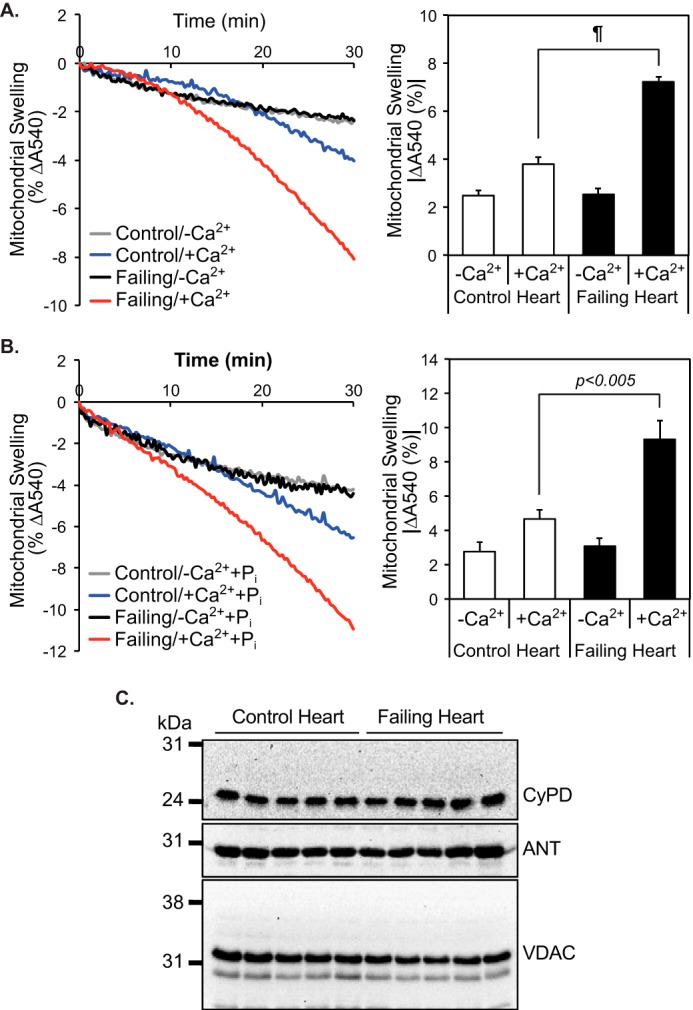
Increased sensitivity of mitochondria from failing human myocardium to calcium-induced swelling in comparison with non-failing mitochondria. Mitochondria were isolated from non-failing and failing hearts by differential centrifugation and resuspended in Mitochondrial Swelling Buffer (3 mm HEPES (pH 7.4), containing 0.23 m mannitol, 0.07 m sucrose, 5 mm succinate, and 2.5 μm rotenone) in the absence (n = 14 for non-failing controls and n = 12 for failing hearts) (A) or presence of 1 mm Pi (n = 4 for non-failing controls and n = 5 for failing hearts) (B). Mitochondrial swelling was initiated by addition of 70 μm Ca2+ and monitored by the decrease in absorbance at 540 nm (A and B, left panels). The average decrease in absorbance at 540 nm after 30 min was calculated (A and B, right panels, average ± S.E.). ¶, p < 10−6. C, protein expression levels of CypD, ANT, and VDAC in non-failing control (n = 5) and failing hearts (n = 5).
