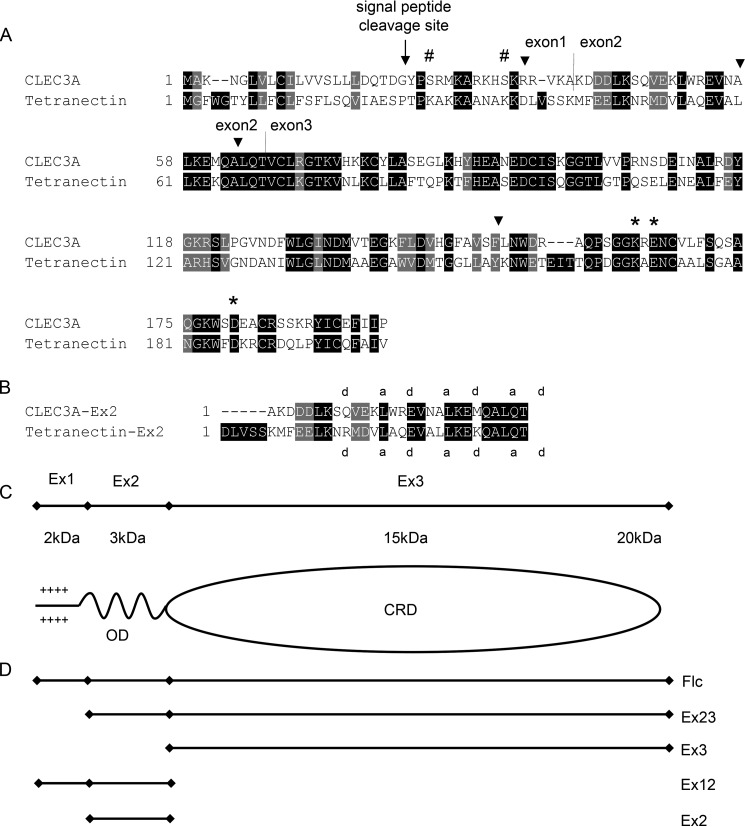
Figure 1.
Alignment of CLEC3A and tetranectin and schematic illustration of CLEC3A. A, alignment of the amino acid sequence of mouse CLEC3A (NM_001007223.3) and mouse tetranectin (NM_011606.2). The potential signal peptide cleavage site is marked by an arrow, exon/intron borders of exons 1, 2, and 3 by vertical lines (2), and MMP-7 cleavage sites by arrowheads (9). The amino acid sequences of mouse and human CLEC3A show a homology of 87%. Three amino acids that are involved in binding the plasminogen kringle 4 domain are conserved in mouse and human CLEC3A (asterisks). Hash mark, predicted O-glycosylation sites; the illustration is based on Ref. 2. B, alignment of the murine CLEC3A and murine tetranectin sequences encoded by exon 2. The positions “a” and “d” that are preferentially occupied by hydrophobic amino acids in heptad repeats are indicated (15). C, schematic depiction of CLEC3A. OD, potential oligomerization (coiled-coil) domain. CRD, carbohydrate recognition domain. D, schematic illustration of recombinant full-length CLEC3A and truncated forms of CLEC3A.