Figure 2.
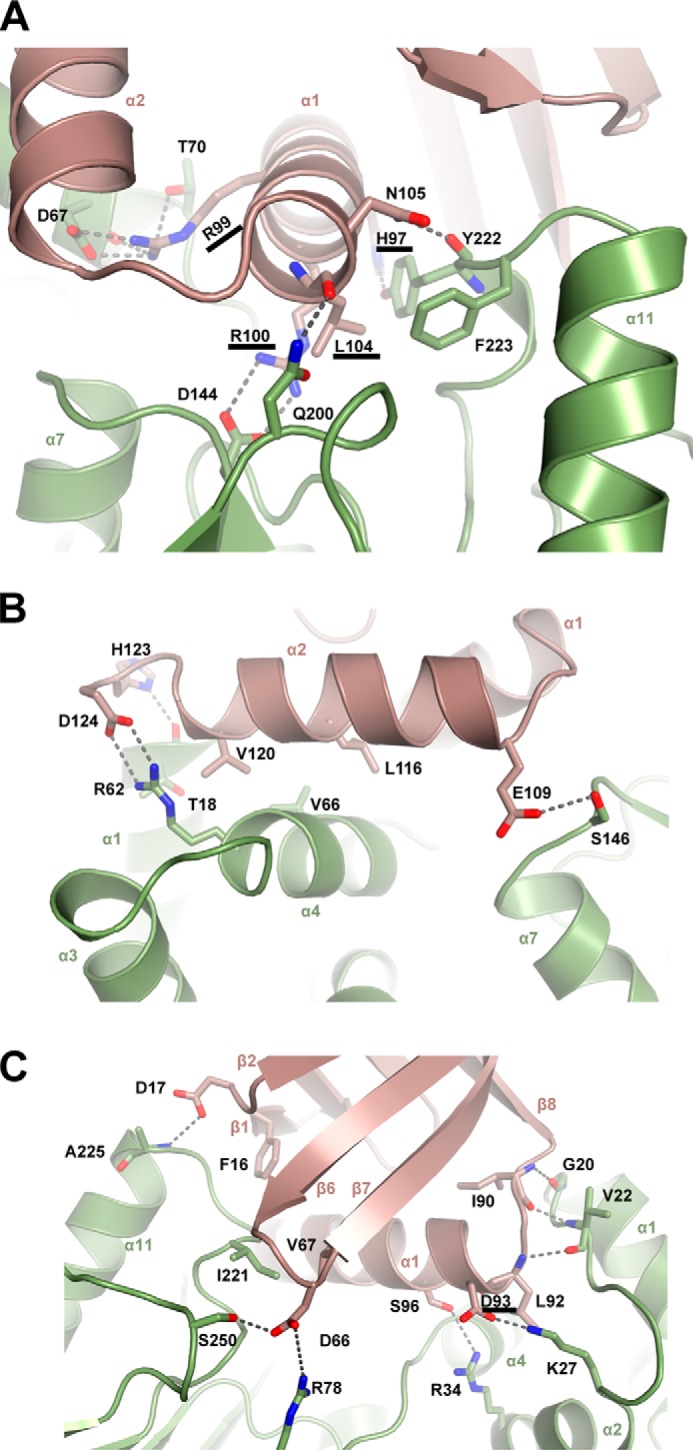
Specific interactions that stabilize the MapZ–c-di-GMP–CheR1 ternary complex. A, specific interactions involving residues from the helix α1 of MapZ. Helix α1 (aa 92–106) is positioned in the central cleft of CheR1 to form extensive contacts, including salt bridges for Arg99-Asp67 and Arg100-Asp144; hydrogen bonds for His97-Tyr222, Arg99-Thr70, Leu104-Asn200, and Asn105-Tyr222; and hydrophobic interactions for Leu104-Tyr222 and -Phe223 (the former residues in the pairs are from MapZ; same as below). B, specific interactions involving helix α2 and adjacent loops of MapZ. The residues in α2 and the adjacent loops in MapZ mainly interact with the N-terminal domain (α1 and α4) of CheR1. C, specific interactions involving residues from the non-C-terminal regions of MapZ. The N-terminal β1-β2 loop and β6-β7 loop in MapZ contact the C-terminal domain of CheR1, and the loop residues Ile90 and Leu92 between β8 and α1 engage in hydrogen-bonding interactions with the N-terminal loop (α1-α2) residues Gly20 and Val22 in CheR1. For clarity, the residues Asp93 and Ser96 from α1 of MapZ interacting with Lys27 and Arg34 of CheR1 are shown in this panel instead of in A. Note that residues involved in the above interactions are shown as sticks with oxygen and nitrogen atom colored red and blue, respectively. Hydrogen bonds and salt bridges are shown as dashed lines. The residues involved in critical interactions are underlined.
