Figure 1.
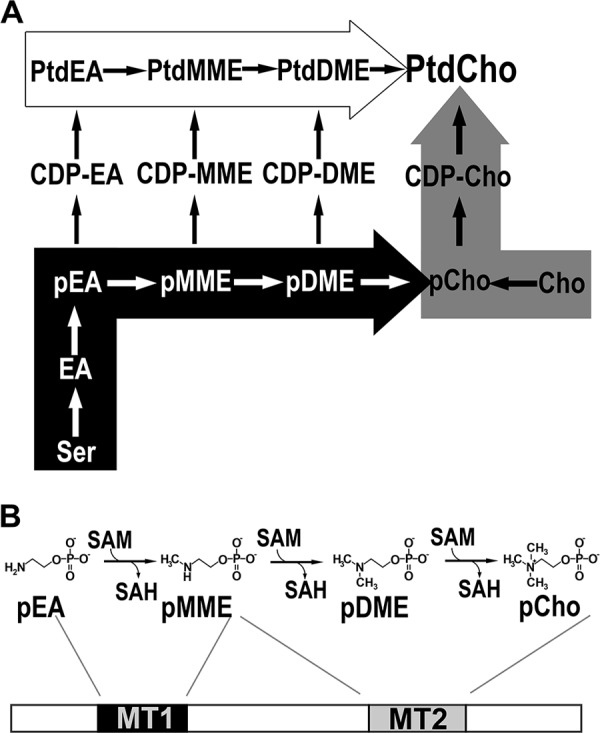
Plant phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis and the di-domain architecture of the type I PMT from plants. A, phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis. The de novo choline or Kennedy pathway (gray arrow), the Bremer-Greenberg pathway (white arrow), and the phosphobase methylation pathway (black arrow) are shown. Metabolite names consist of a prefix (p, phospho; CDP-, cytidine 5′-diphosphate; or Ptd, phosphatidyl) and a core name (EA, ethanolamine; MME, monomethylethanolamine; DME, dimethylethanolamine; Cho, choline). B, reactions and domain structure of the type I PMT from plants. Methylation of phosphoethanolamine (pEA) to phosphomethylethanolamine (pMME) is catalyzed by the first methyltransferase domain (MT1) and the methylation reactions converting pMME to phosphocholine (pCho) catalyzed by the second methyltransferase domain (MT2).
