Figure 3.
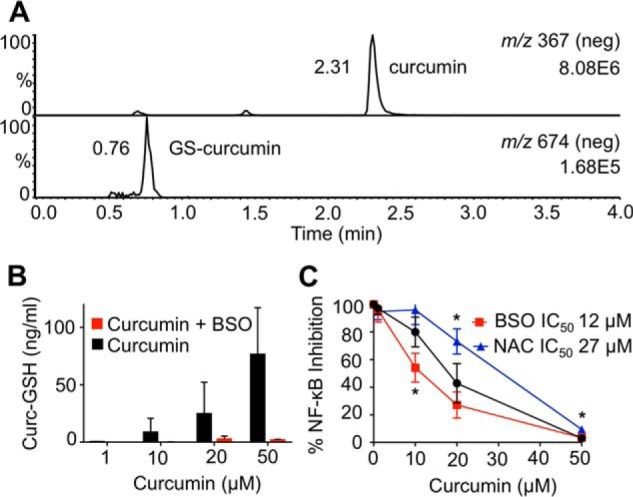
Modulation of glutathione changes the anti-inflammatory effect of curcumin. A, LC-MS detection of curcumin (top) and its glutathione adduct (bottom) in the supernatant of RAW264.7 cells. B, LC-MS quantification of curcumin-glutathione adducts with and without pretreatment with BSO. C, RAW264.7 cells were pretreated with BSO, NAC, or vehicle for 24 h prior to addition of curcumin, and the IC50 for inhibition of LPS-induced NF-κB activity was determined. *, p < 0.05 versus curcumin (n = 3).
