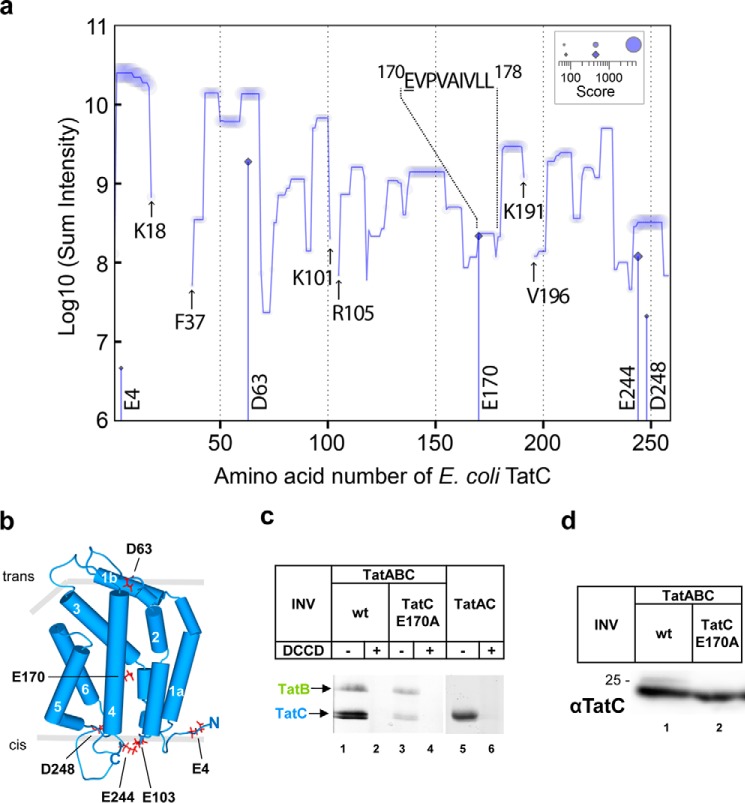
Figure 2.
Glutamate 170 of E. coli TatC becomes quantitatively modified by DCCD. a, sequence coverage and sites of modification by DCCD of E. coli TatC analyzed by quantitative mass spectrometry. For each amino acid along the sequence of TatC, MS intensities of peptides containing this residue were summed up and plotted against its sequence residue number. Relative quantification of peptides was performed based on detected ion intensities. Peptide scores are indicated and reflect the probability-based significance of peptide identifications based on matched fragment ions in MS/MS spectra. The sum of peptide scores per amino acid is decoded by the size of the symbols. Indicated are amino acids flanking the three sequence sections of DCCD-treated TatC that were not covered by the MS/MS analysis (arrows). Cumulative intensities of peptides identified with modification of aspartic or glutamic acid by DCU are plotted at positions of the modified sites (diamonds on vertical lines) according to the same logarithmic scale as the total sum of intensities including modified and unmodified peptides. Virtually 100% of the peptide 170EVPVAIVLL178 depicted was found modified by DCU. b, model of the E. coli TatC structure adapted from the crystal structure of A. aeolicus TatC (PDB codes 4B4A and 4HTT) (11, 12) with the six transmembrane helices and the N and C termini marked. Residue Glu170, which is virtually completely modified by DCCD, and the other DCCD sensitive residues are marked in red. The bilayer is outlined by gray bars, the cis-side corresponds to the cytoplasmic face of E. coli TatC. c, vesicles (INV) were prepared from E. coli strains overexpressing TatABC (wt), TatABCE170A, and TatAC. INV were either treated with DCCD or DMSO before incubating with the fluorescent DCCD analogue NCD-4. Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed under UV light. d, Western blot analysis using anti-TatC antibodies to demonstrate unimpaired expression of the E170A variant of TatC.