Figure 5.
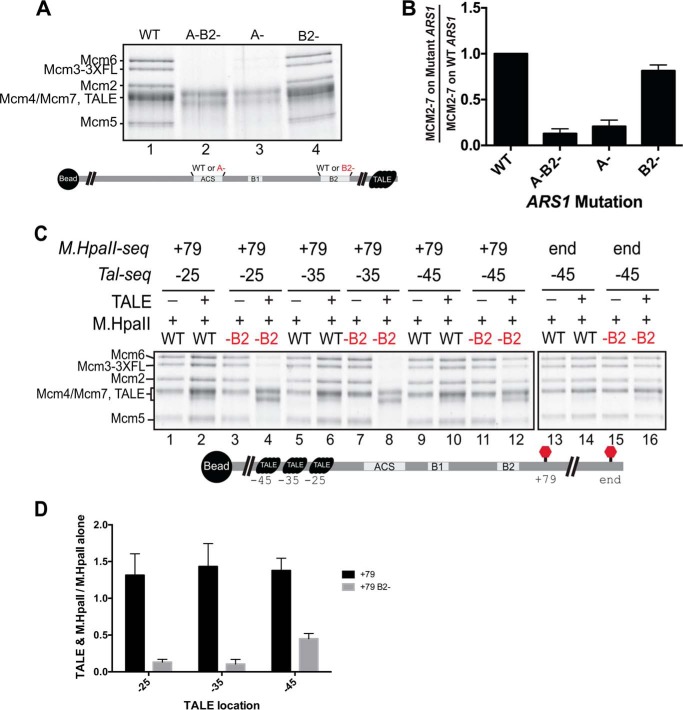
ARS1-flanking roadblocks lead to enhanced B2 requirement for Mcm2-7 loading. A, Mcm2-7 loading following a high-salt wash using the wild-type and mutant ARS1 DNA templates. Comparison of the sequences between different mutant origin templates are shown in Fig. S9. B, quantification of the relative amount of helicase loading for mutant ARS1 DNA templates. The level of Mcm2-7 loading for wild-type ARS1 DNA was set to 1, and the relative ratio of Mcm2-7 loading for each mutant DNA is reported. Error bars are the standard deviation from the mean calculated for three independent experiments. C, impact of B2 mutation on Mcm2-7 loading onto ARS1 DNA with or without ARS1-flanking DNA roadblocks. ARS1 DNA templates with or without a mutation in B2 were cross-linked to M.HpaII either at +79 or the DNA end. These templates were tested for salt-stable Mcm2-7 loading with or without TALE binding to one of three sites as indicated. The location of the 5FdC-modified M.HpaII recognition motif (M.HpaII-seq) and the location of the TALE-binding sequence (Tal-seq) are noted above each pair of lanes. D, quantitation of relative Mcm2-7 loading with or without ARS1-flanking DNA roadblocks. The ratio of Mcm2-7 loading with and without a second (TALE) roadblock is reported for ARS1–DNA templates with M.HpaII cross-linked at position +79 with or without a B2 mutation. Error bars are the standard deviation from the mean calculated for three independent experiments.