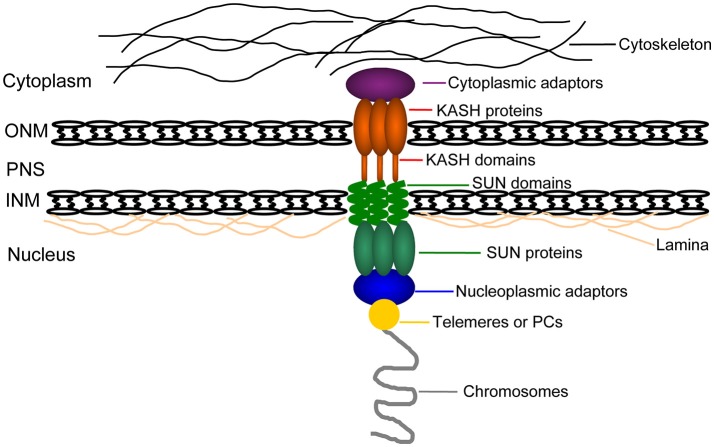
Figure 3.
A schematic representation of the link transferring cytoplasm forces into meiotic chromosomes. Telomeres or PCs (gold circle) connect to the NE through nucleoplasmic adaptors (schematized with a blue oval) and the nucleoplasmic domains (in green ovals) of SUN-domain proteins spanning the INM (in green; shown as a trimer). KASH domain proteins span the ONM (in red; shown as a trimer). Then SUN domains (in green helix) can interact with KASH domains (in red stub) in the PNS. Cytoplasmic adaptors (in purple) connect the cytoplasmic domains (in red ovals) of KASH proteins to the cytoskeleton (in black lines). The nucleoplasmic domains of SUN proteins can also interact with lamins (in orange). Cytoskeleton, cytoplasmic adaptors, SUN-KASH protein bridges, nucleoplasmic adaptors and telomeres/PCS form the central link that spans the nuclear envelope, transferring cytoplasm-derived forced into chromosomes. NE, nuclear envelope; INM, inner nuclear membrane; ONM, outer nuclear membrane; PNS, the perinuclear space.