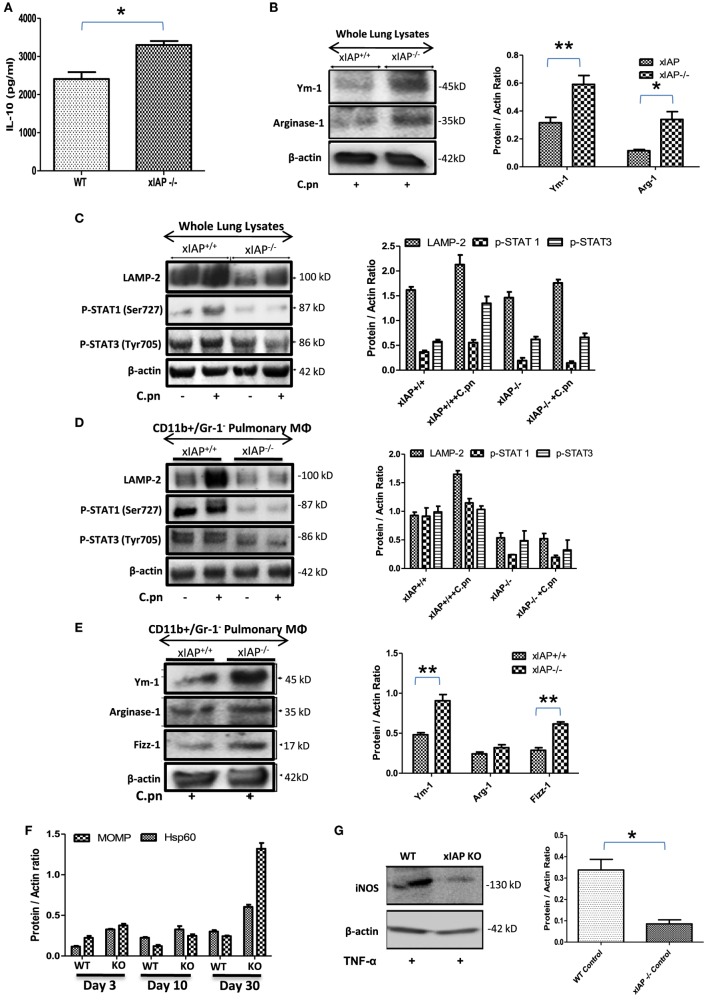
Figure 1.
XIAP deficiency promotes M2 polarization during the course of infection. (A) Pulmonary titer of IL-10 in xIAP KO mice and its WT counterpart at 20th post infection day was analyzed by sandwich ELISA. (B–E) Whole lung tissue and CD11b+/Gr-1 (−) pulmonary macrophage cell lysates from both WT and Xiap KO mice 20 days after Chlamydia pneumoniae infection were analyzed by Western blotting for M1 and M2 signaling markers. (F) Expression of chlamydial HSP60 and major outer membrane proteins in the lung of XIAP KO-infected mice with time and (G) expression of iNOS protein in XIAP-deficient CD11b+/Gr-1 (−) pulmonary macrophages over WT counterpart in response to TNF stimulation were analyzed by Western blotting. 20 µg of protein per sample was analyzed by the immunoblot method as described in the “Materials and Methods” section. β-actin was used as a loading control. Representative blots from three independent mice infections with similar outcome are shown. The Western blots were quantified for densitometry by Image J software, and mean densitometry values of independent proteins were divided with its mean densitometry values of its respective β-actin band intensity value to present the relative expression of each protein as a mean in the ratio of protein to actin. Data shown here is the ±SEM from three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was conducted either by using two-tailed unpaired t-test and/or by using two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-test, respectively (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; and ***p < 0.001).