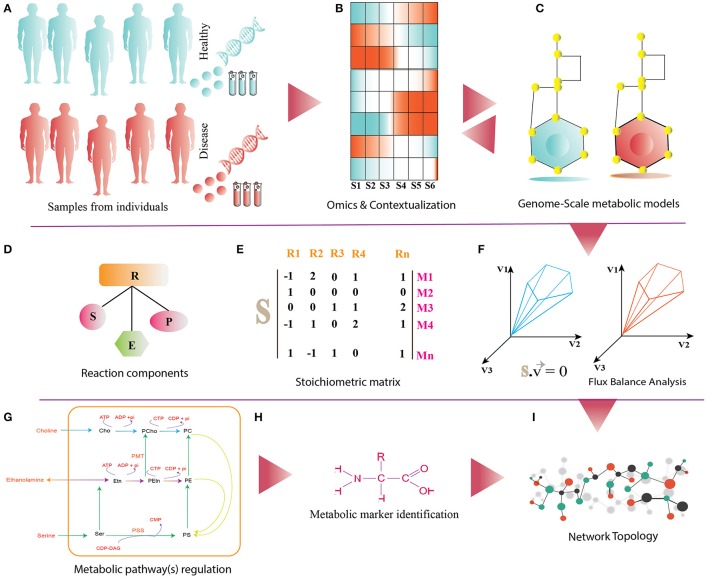
Figure 2.
(A) It shows disease and healthy individuals (controls) from which PBMCs samples are obtained for omics analysis. (B) Differential omics expression and analysis for contextualization. (C) Reconstruction and contextualization of condition specific genome-scale metabolic models. (D) Reaction components (R) of Genome-Scale metabolic models: S, substrates; E, enzymes; P, products. (E) Stoichiometric matrix (S) of Mn metabolites and Rn reactions, directionality of each metabolites consumed (−1) or produced (+1) or not involved in the reaction (0). (F) Flux-Balance Analysis (FBA) for model simulation, optimization and estimation of flux (v) phenotype at the steady state. (G–I) The panel shows functionalities of genome-scale metabolic models such as regulations of metabolic pathway, metabolic marker identification and identification of differential pathways.