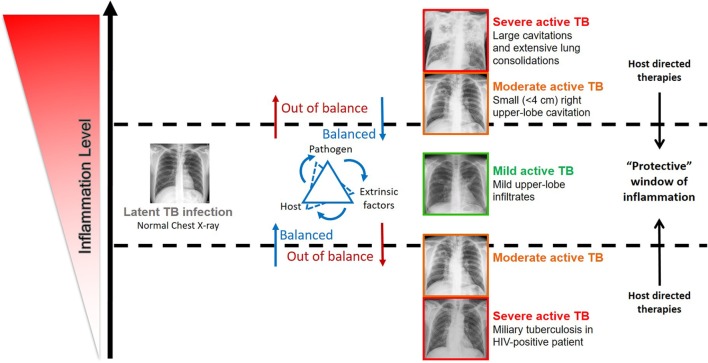
Figure 1.
Impact of the inflammation level in the disease outcome in individuals infected by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The spectrum of tuberculosis (TB) disease is strongly linked with the host immune status. The inflammation level results from the interaction of host, pathogen, and extrinsic factors. Very low and high inflammation levels often associated with severe active TB, while balanced immune responses associated with mild active TB, latent TB, and possibly TB clearance. Evidence supports that host-directed therapies (see Table 1) have the potential to successfully modulate inflammation and ameliorate disease outcome, by ensuring a protective immune response.