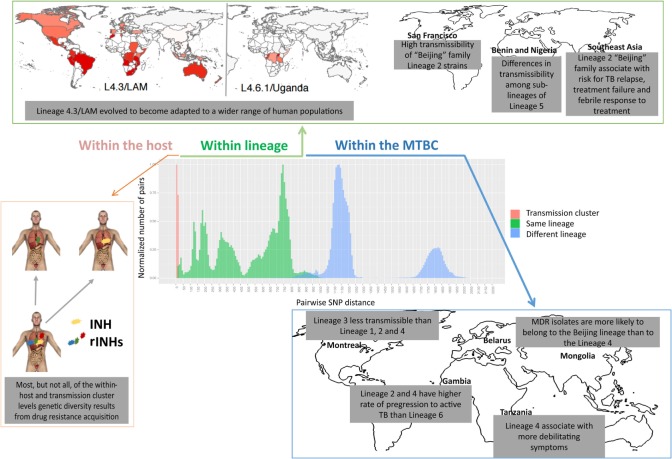
Figure 3.
Levels of genetic diversity across the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTBC) and its epidemiological and clinical impact. There are different levels of diversity across the MTBC. Within a host or transmission chain, M. tuberculosis isolates typically differ in less than 25 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Diversity increases when comparing isolates within the same lineage (around 25–1,000 SNPs) or within different lineages of the MTBC (around 1,000–2,000 SNPs). This diversity impacts host/pathogen interactions, particularly the intensity and quality of the immune response and the clinical outcome, at the levels of drug acquisition, adaptation to different populations, transmissibility, or disease manifestation.