Figure 3.
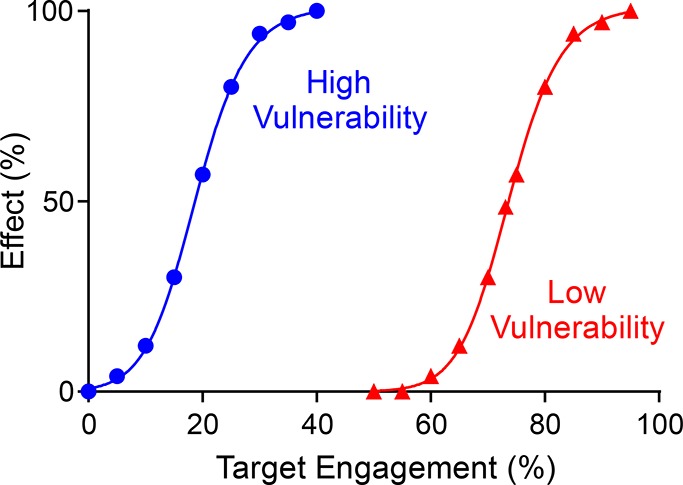
Target vulnerability plots. Vulnerability functions are shown for low (red) and high (blue) vulnerability targets. The vulnerability function is defined by the minimum level of engagement required for any effect to be observed (TOmin) and the level of engagement that leads to the maximal efficacy (TOmax). The third parameter required to define the function is the Hill coefficient or slope factor that determines the steepness of the effect response between TOmin and TOmax. For the low vulnerability target, the full physiological effect of the drug requires close to 100% target engagement, whereas only ∼35% engagement is needed for the high vulnerability target. The Hill coefficients for the two functions are 4.6 (high) and 16.4 (low).
