Figure 7. Increased serotonin dependence of hindlimb locomotor CPG output following Lb‐SCC.
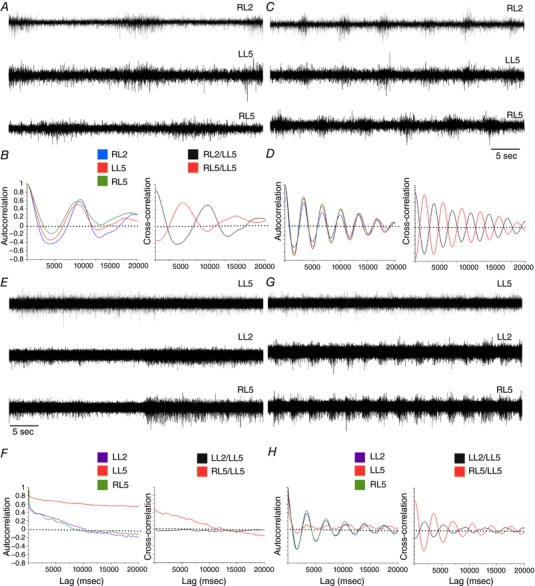
A–D, serotonin dependence in control spinal cords. Representative raw ventral root recordings from control spinal cords prior to (A) and after serotonin application (C) during rhythmic activity elicited by a reduced neurochemical cocktail (NMDA, 5 μm; DA, 50 μm). B and D, auto‐ and cross‐correlations for the traces shown in A and C, respectively. A slow rhythmic output can be elicited without serotonin, but addition of serotonin increases frequency markedly to match that of bona fide fictive locomotion. E–H, serotonin dependence in P4 Lb‐SCC preparations. Representative raw ventral root recordings from a Lb‐SCC spinal cord prior to (E) and after serotonin application (G) while in the presence of the reduced neurochemical cocktail (NMDA, 5 μm; DA, 50 μm). F and H, auto‐ and cross‐correlations for the traces shown in E and G, respectively. The non‐oscillatory, decaying cross‐correlations in F indicate a lack of rhythmicity in the absence of serotonin. Rhythmicity is instated following serotonin application, as shown by the oscillatory auto‐ and cross‐correlation functions in H.
