Figure 5.
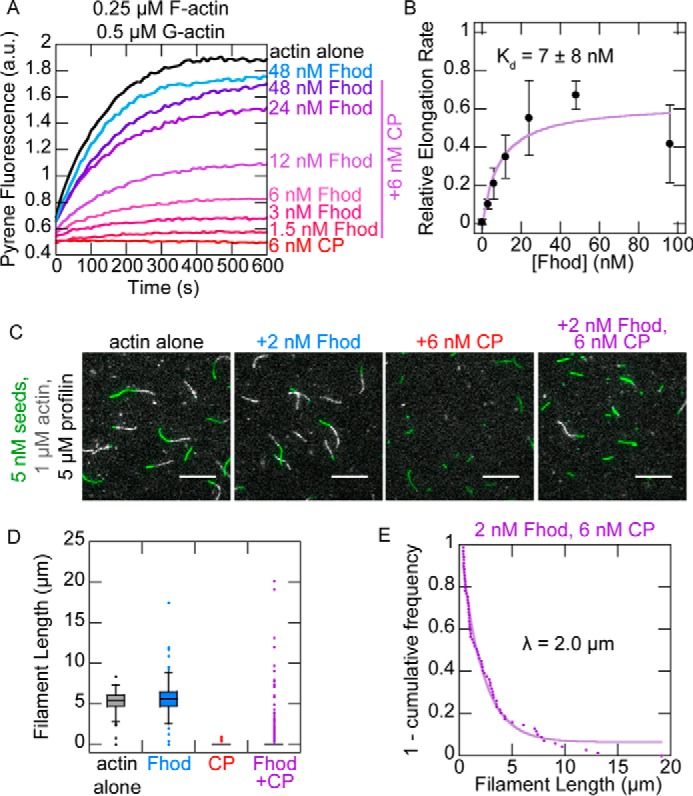
Fhod antagonizes capping protein. A, actin elongation from preformed seeds with a range of Fhod concentrations added before capping protein. Final conditions were 0.25 μm F-actin seeds (∼0.4 nm barbed ends), 0.5 μm G-actin (10% pyrene-labeled), 1.5 μm S. pombe profilin, ± 6 nm mouse capping protein and 1.5–48 nm Fhod. B, quantification of elongation rates from A, measured as the initial slope over the first 90 s relative to the slope of actin alone. Fhod antagonizes capping protein, allowing elongation. Data with Fhod and capping protein were fit to a competition binding model to determine the affinity of Fhod to barbed ends. The data and reported Kd are means ± standard deviation from four independent experiments. The binding curve shows the best fit to the average values. C, observation of actin elongation (white) from preformed seeds (green) with Fhod added before capping protein. Final conditions were 5 nm F-actin seeds (1% biotinylated, labeled with Alexa Fluor 647-phalloidin), 1 μm G-actin (10% Alexa Fluor 594-labeled), 5 μm S. pombe profilin, ± 2 nm Fhod, and 6 nm capping protein. Images were taken 5 min after initiation of polymerization. Scale bars, 10 μm. D, quantification of filament lengths from C. The data represent the amount of elongation from preformed seeds (n > 150 for each condition). At least five fields of view from one (actin alone) or two (all other conditions) flow chambers were analyzed for each condition. In conditions with capping protein, no box is visible because over 75% of seeds did not elongate. E, exponential fit of filament lengths in the presence of both Fhod and capping protein from D, excluding seeds that did not elongate (n = 69 filaments from two flow chambers). Fhod has a characteristic run length of 2.0 μm.
