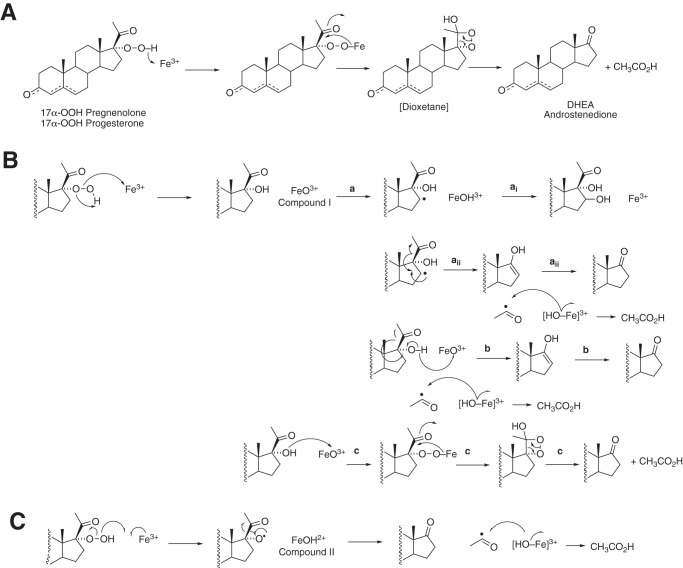
Figure 10.
Possible pathways for decomposition of 17α-OOH steroids. A, dioxetane mechanism. B, formation of Compound I (FeO3+) by heterolytic cleavage of 17α-OOH steroids. The a reactions are the result of C–H hydrogen abstraction reactions, and reactions similar to ai are proposed to result in the observed 6β- and other hydroxylations (Fig. 2, Table S2, and Figs. S5–S7). Reaction b involves abstraction of a hydrogen atom from the 17α-OH group and leads to the lyase product. Reaction c results from the reaction of the nucleophilic 17α-alcohol with Compound I and parallels the dioxetane mechanism in A. C, homolytic scission of the 17α-OOH steroid yields Compound II. The mechanism can explain the lyase products but not the hydroxylations.