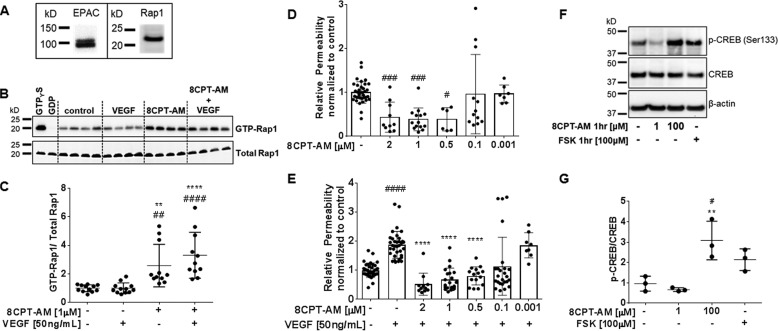
Figure 2.
8-CPT-AM Rap1 activation prevents VEGF-induced permeability of BREC. A, Western blot analysis from BREC lysates shows the presence of the GEF EPAC1 and small G-protein Rap1. B, GTP bound Rap1 was determined by capture assay using GST-RalGDS RBD. 8-CPT-AM (1 μm) was added 30 min prior to VEGF (50 ng/ml) for a total time of 1.5 h. Assay controls GTPγS and GDP were added to lysates before capture. Quantification is shown in C with a total n ≥ 11. D, solute flux assay was used to test permeability to 70-kDa RITC-dextran after 8-CPT-AM at varying concentrations on BREC, n ≥ 6. E, 8-CPT-AM prevents VEGF-induced permeability. BREC stimulated with 8-CPT-AM at the doses indicated are 30 min prior to VEGF addition. Doses from 0.5 to 2 μm blocked VEGF-induced permeability. Average Po values for control were 7.1 × 10−7 and VEGF were 1.4 × 10−6 (cm/s), total of n ≥ 8. F, low dose 8-CPT-AM does not activate the PKA pathway. 8-CPT-AM at 1 μm was added to BREC for 1 h and no increase in CREB phosphorylation was observed. Incubation of 8-CPT-AM or forskolin (FSK) at 100 μm for 1 h increased CREB phosphorylation. G, quantification shown in F with a total n ≥ 3. All results are expressed as the mean ± S.D. relative to the control. One-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test: #, p < 0.05; ##, p < 0.01; ###, p < 0.001; ####, p < 0.0001 compared with control in C–E and G. **, p < 0.01; ****, p < 0.0001 compared with VEGF in C and E or 8-CPT-AM (1 μm) in G.