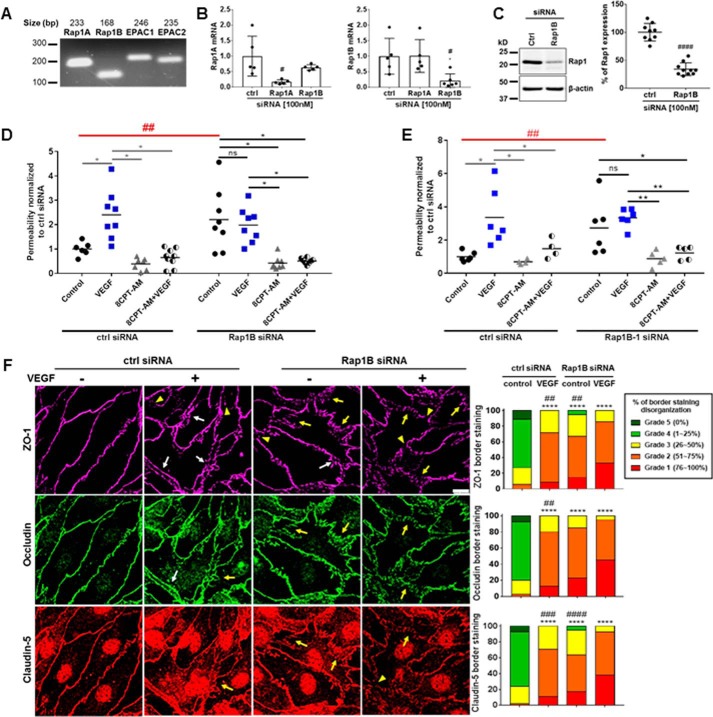
Figure 7.
Rap1B contributes to basal permeability and tight junction organization. A, both Rap1 (Rap1A and Rap1B) and EPAC (EPAC1 and EPAC2) isoforms were found to be present in BREC by PCR. B, SYBR Green qRT-PCR was used to test Rap1 isoform siRNAs specificity. #, p < 0.05. C, Western blot shows that composite Rap1B (100 nm) siRNA results in a 66% knockdown, Student's t test ####, p < 0.0001, n ≥ 9. D, solute flux assay was used to test permeability in BREC with Rap1B knockdown. Scramble and Rap1B siRNA at 100 nm were used in BREC. Average Po values for scramble control and Rap1B siRNA control were 2.4 × 10−7 and 5.4 × 10−7 (cm/s). E, solute flux assay was used to test permeability in BREC with individual Rap1B-1 siRNA. Scramble and Rap1B-1 siRNA at 100 nm were used in BREC. Average Po values for scramble control and Rap1B-1 siRNA control were 9.0 × 10−8 and 2.3 × 10−7 (cm/s). F, immunofluorescence staining of TJ proteins ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-5 was performed to assess the organization of TJ proteins after Rap1B knockdown with and without VEGF (50 ng/ml) for 1 h. Scale bar, 10 μm. Histograms of scoring TJ show % organization of TJs. All results are expressed as the mean relative to the scramble control with a total of n > 4. ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-5 border staining were assessed by semi-quantitative ranking score system based on scale grades from 1 to 5. Immunofluorescence results are expressed as the mean relative to the scramble control n ≥ 4 with analysis by one-way analysis of variance and Bonferroni post hoc test, ****, p < 0.0001 compared with scramble control and ##, p < 0.05; ###, p < 0.001; ####, p < 0.0001 compared with Rap1B siRNA VEGF. Permeability results are expressed as the mean relative to the scramble control two-way analysis of variance analysis and Bonferroni post hoc test: *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; and ##, p < 0.01 comparison between scramble and Rap1B or Rap1B-1 siRNA controls.