Figure 6.
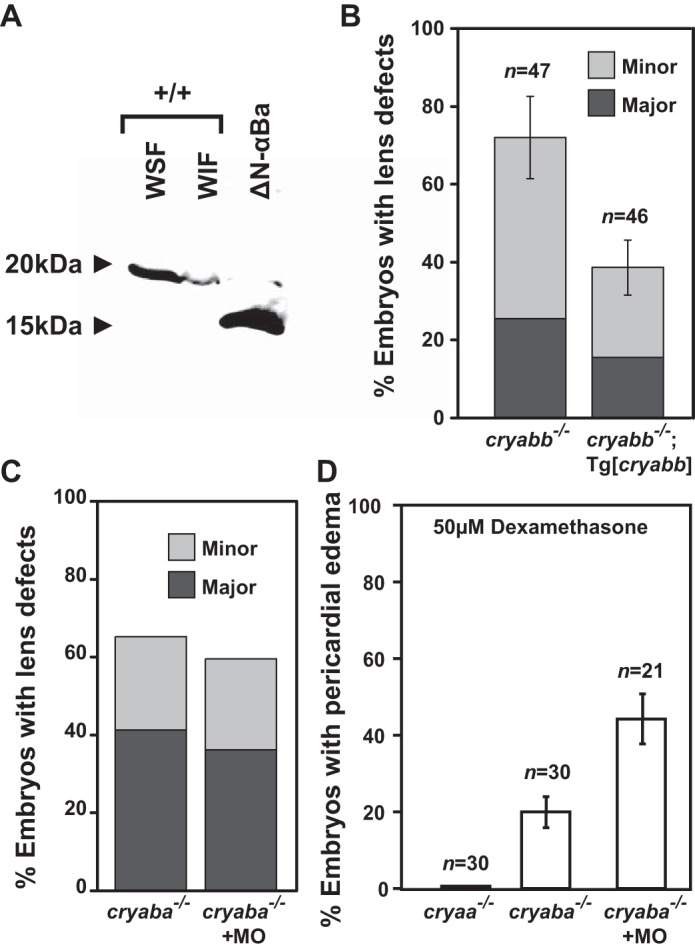
αB-crystallin mutations function as loss-of-function alleles. A, purified N-terminal truncated (Δ1–43 amino acids) αBa protein (bacterial expression) was detectable by anti-αBa polyclonal antibody. The WSF and WIF protein fractions of the excised lenses of the wild-type adult zebrafish served as control, stained for full-length αBa protein. B, transgenic expression of zebrafish αBb (Tg[cryabb]) in the lens of αBb−/− embryos showed suppression for its lens defects, compared with non-transgenic siblings (αBb−/−). C, percentage of embryos with lens defects remained unchanged in αBa−/− embryos injected a morpholino (MO) interfering with the alternative start site compared with control αBa−/− embryos. D, GR activation-induced (50 μm dexamethasone) pericardial edema in αBa−/− embryos was not suppressed by injecting morpholino interfering with the alternative start site. In addition, αA−/− embryos showed no heart edema when treated with dexamethasone.
