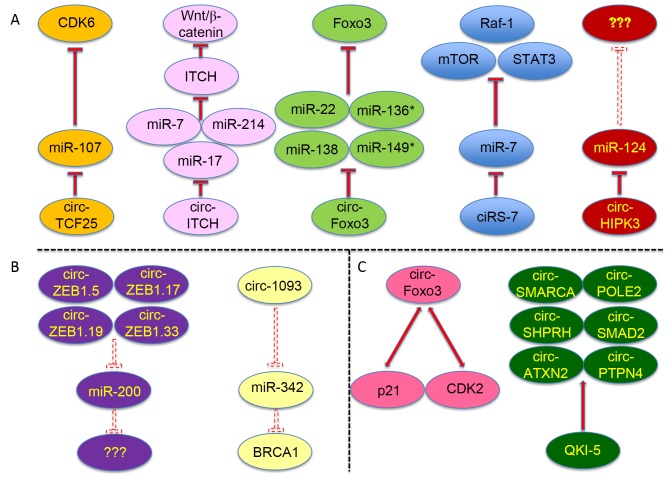
Figure 2.
Circular RNAs function as competing endogenous RNAs in multiple types of cancer. The specific microRNAs and RNA-binding proteins sponged by certain circular RNAs are shown, as well as the protein targets of certain sponged miRNAs. (A) Specific and validated microRNAs sponged by certain circular RNAs, as well as the protein targets of certain sponged miRNAs. (B) Predicted microRNAs sponged by certain circular RNAs. (C) Validated and specific RNA-binding proteins sponged by certain circular RNAs. The dashed inhibition arrows represent predicted but not validated inhibitory effects, and the solid inhibition arrows represent that the inhibitory effects have been experimentally validated. ‘???’ denotes that the targeted genes of the microRNAs were not addressed in the corresponding reference. circ, circular RNA; miR, microRNA; CDK, cyclin-dependent kinase; TCF25, transcription factor 25; ITCH, itchy E3 ubiquitin protein ligase; Foxo3, forkhead box O3; Raf-1, Raf-1 proto-oncogene; mTOR, mechanistic target of rapamycin; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; HIPK3, homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 3; ZEB, zinc finger E-box binding homeobox; SMARCA, SWI/SNF-related, matrix-associated, actin-dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily A; POLE2, DNA polymerase ε2, accessory subunit; SHPRH, SNF2 histone linker PHD RING helicase; SMAD2, SMAD family member 2; ATXN2, ataxin 2; PTPN4, protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 4; QKI-5, Quaking 5.