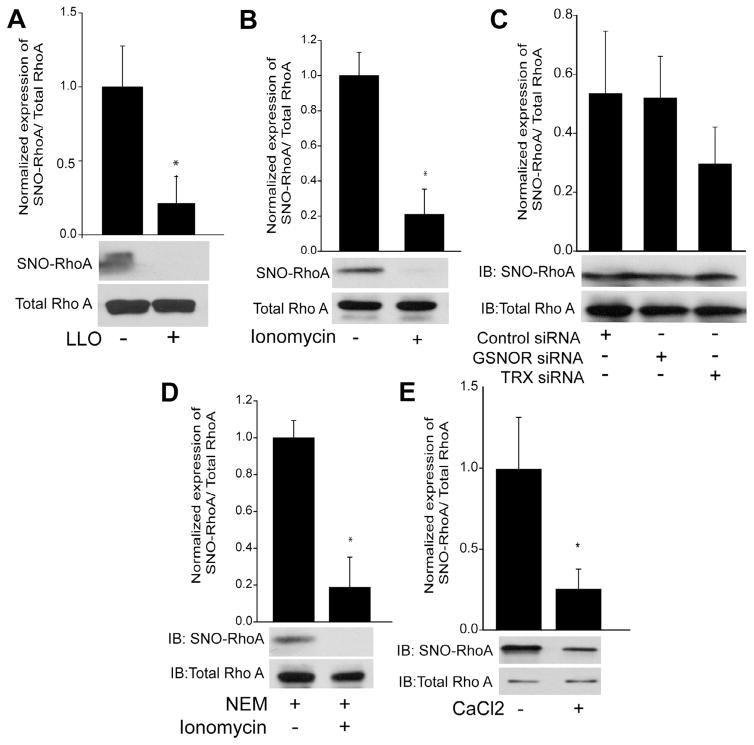
Fig. 7.
Denitrosylation of RhoA is mediated by calcium and not the denitrosylates GSNOR and TRX. (A-B) HEK293-eNOS cells were transfected with WT RhoA for 48 h and then treated with or without LLO (250 ng/ml), the selective calcium ionophore, ionomycin (1 μM) for 30 min. The degree of RhoA S-nitrosylation was determined by the biotin-switch assay, and the relative densitometric ratio of SNO-RhoA (top panel) vs total-RhoA (bottom panel) determined. (C) HEK293-eNOS cells expressing RhoA were transfected with a scrambled negative control siRNA or siRNAs targeting GSNOR or TRX, exposed to ionomycin (1 μM) for 30 min and the level of S-nitrosylated RhoA determined by the biotin-switch assay and shown by the relative densitometry of SNO-RhoA (top panel) vs total-RhoA (lower panel). (D) HEK293-eNOS cells transfected with WT RhoA for 48 h were treated with NEM (40 mM) to block free thiol groups, and then stimulated with or without ionomycin (1 μM) for 30 min. S-nitrosylated RhoA was determined by the biotin-switch assay, and the relative densitometry of SNO-RhoA (top panel) vs total-RhoA (lower panel) determined. (E) Recombinant RhoA was nitrosylated with 100 μM Cys-NO for 30 min and then exposed to 3 mM CaCl2 for 1 h. The level of S-nitrosylated RhoA was determined by the biotin-switch assay, and shown by the relative densitometry of SNO-RhoA (top panel) vs total-RhoA (lower panel). Data are expressed as means ± S.E., *P < 0.05 versus control. (n = 3–4).