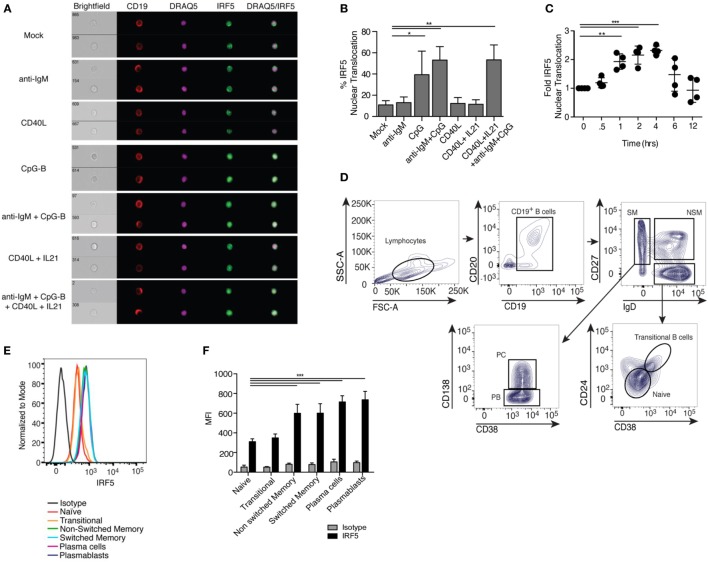
Figure 1.
Toll-like receptor 9/B cell receptor stimulation induces Interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) nuclear translocation. (A) Representative images of IRF5 cellular localization in human CD19+ B cells from a single healthy donor that were stimulated with mock, anti-immunoglobulin (Ig) M antibody, CD40 ligand (CD40L), CpG-B, or CD40L and IL21, and the combination of anti-IgM antibody, CD40L, IL21, and CpG-B for 2 h. PBMC were surface-stained with anti-CD19 antibodies, fixed and permeabilized, then stained for intracellular IRF5 and nuclear DRAQ5. Samples were then subjected to imaging flow cytometry followed by analysis in the IDEAS software suite. (B) Frequency of cells in (A) with IRF5 nuclear translocation, which was defined by an IRF5 and DRAQ5 similarity score ≥2 (one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test; n = 4 independent donors). (C) IRF5 nuclear translocation was quantified over 12 h in isolated B cells following stimulation with anti-IgM+ CpG-B. Data was normalized to mock to minimize donor variability (one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test; n = 4 independent donors). (D) Representative gating strategy for human B cells subsets in peripheral blood of healthy donors who received the influenza vaccine 7 days prior to phlebotomy. B cell populations were defined as CD19+CD20+ naive (IgD+CD38−CD27−CD24−), transitional (IgD+CD27−CD38+CD24+), non-switched memory (NSM; IgD+CD27+CD38−CD24−), switched memory (SM; IgD−CD27+CD24−), plasma blasts (PB; IgD−CD38hiCD27+CD24−CD138−), and plasma cells (PC; IgD−CD38hiCD27+CD24−CD138+). (E) Representative histograms of IRF5 protein expression in B cell subsets gated in (D). (F) Average MFI of IRF5 expression in gated B cell subsets (two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison post hoc test; n = 5 independent donors). Error bars represent SD. *p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.001.