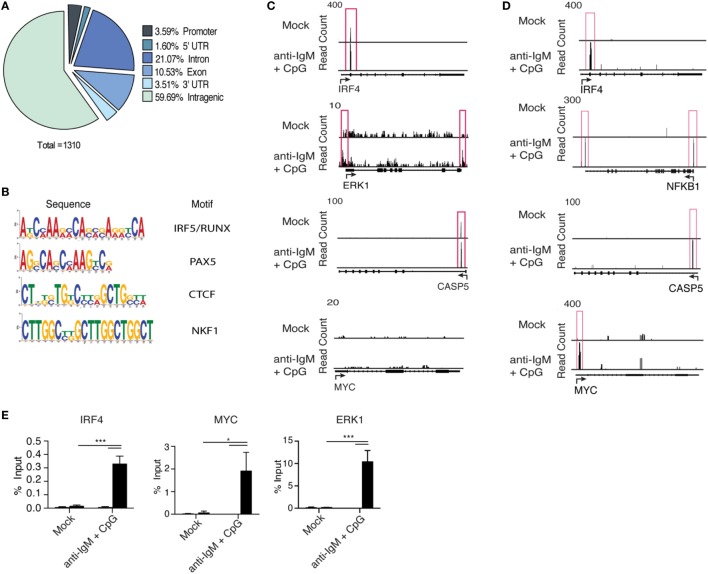
Figure 4.
Interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) binds promoter regions of genes associated with antibody secreting cell (ASC) differentiation. IRF5 ChIP-Seq was performed on isolated primary naive B cells from n = 2 independent donors. B cells were either mock or anti-IgM+ CpG-B stimulated for 4 h. Reads were mapped through BWA and peaks called through MACs. (A) A pie chart showing representative IRF5 binding elements throughout the human primary B cell genome. (B) Common IRF5 binding motifs identified from ChIP-Seq. Motif sequences are shown in order of enrichment with associated transcription factor motif. (C) Representative peak distributions are shown for IRF4, ERK1, CASP5, and MYC. Peaks are boxed in red and were determined at a significance of p ≤ 0.0001. (D) Same as (C) except IRF5 ChIP-Seq peaks are from the Ramos B cell line. Peaks were determined at p ≤ 10−10. (E) Independent confirmation of IRF5 binding to IRF4, MYC, and ERK1 target sites through ChIP-qPCR in primary naive B cells mock stimulated or stimulated with anti-IgM+ CpG-B for 4 h (two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test; n = 4 independent donors). Error bars represent SD. *p ≤ 0.05; ***p ≤ 0.001.