FIGURE 1.
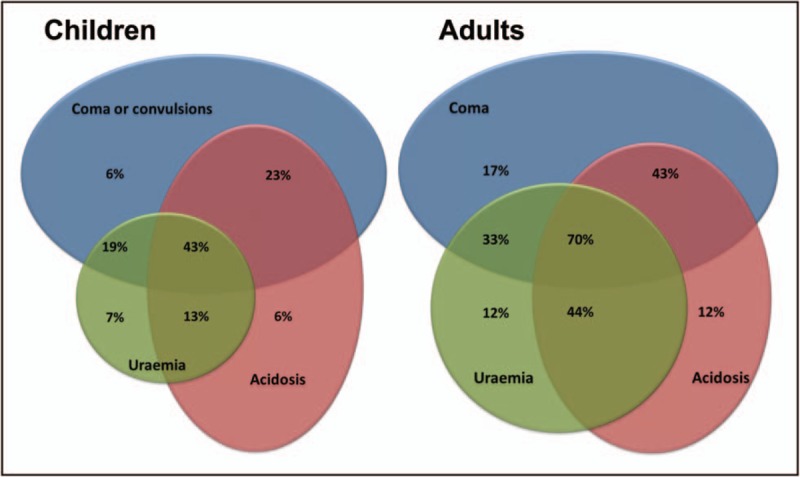
Venn diagrams of mortality of adults and children associated with prognostic manifestations of severe malaria [2,3]. Surface areas represent relative prevalence in severe malaria. Uremia defined as blood urea nitrogen more than 20 mg/dl in children and more than 48 mg/dl in adults. Acidosis defined as base excess less than −8 mmol/l in children and less than −3 mmol/l in adults. Coma score defined as Blantyre Coma Score less than 3 in children and Glasgow Coma Score less than 11 in adults. Reprinted from Tropical Medicine and International Health 19, Supplement 1, World Health Organization, Severe Malaria. Page 16. Copyright (2014).
