FIGURE 3.
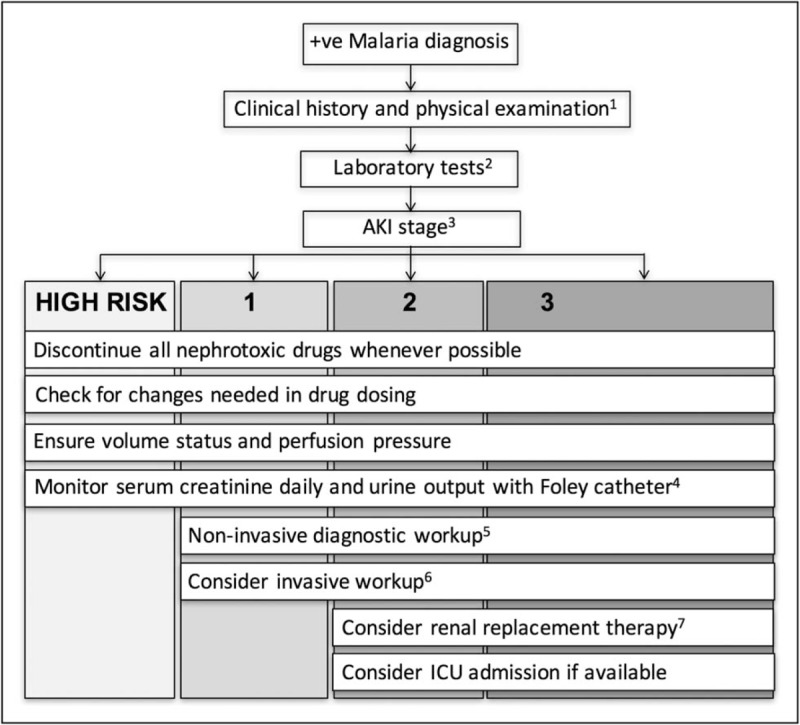
General management of AKI in malaria based on KDIGO guidelines. 1History including preadmission medications, comorbidities, and physical examination focusing on volume status and signs of concomitant sepsis. 2Laboratory tests including serum creatinine, urea, electrolytes, and full blood count. 3Stage using KDIGO staging criteria. If baseline creatinine is unknown, estimate using back-calculation of MDRD equation (>19 years) or Swartz equations (≤18 years). Urinary bladder catheterization to monitor initial urine output if unconscious. If ambulating, urine should be collected to monitor output. Patients should be managed according to AKI stage, as stage correlates with increased morbidity and mortality. 4Daily creatinine and urine output to monitor change in AKI stage severity and guide management. 5Additional investigations to assess AKI etiology: urine analysis, sediment microscopy, creatinine, and sodium; renal ultrasound to assess kidney size, presence of pyelonephritis, and inferior vena cava filling as a gauge of volume status; AKI biomarkers if applicable. Nephrotoxic drugs, that is, aminoglycosides, should be avoided whenever possible. Discontinuation of nephrotoxic drugs may assist with determining AKI etiology. 6If resources permit, monitor hemodynamic variables. Static central venous pressure is of limited value but recommended target is 0 to +5 cmH2O. Arterial pulse pressure as a dynamic variable may be more useful to gauge response to fluid administration. 7Early referral to center with RRT, particularly if one indication for RRT is present. Patients with multiorgan dysfunction are recommended to receive urgent dialysis within 2 h [6]. Patients should be evaluated 3 months after AKI resolution to monitor resolution of kidney function and/or development of chronic kidney disease. AKI, acute kidney injury; KDIGO, Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes; MDRD, modification of diet in renal disease [11]; RRT, renal replacement therapy. Reprinted from Kidney International Supplements 2, Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Acute Kidney Injury Work Group, KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Page 25. Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier.
