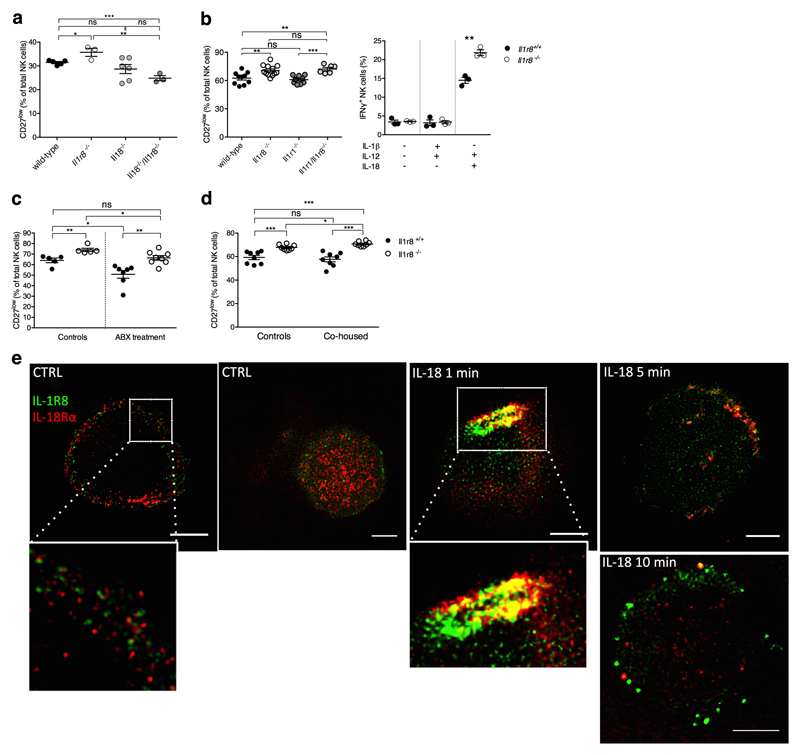
Extended Data Figure 3. Mechanism of IL-1R8-dependent regulation of NK cells.
(a) Splenic CD27low NK cell frequency in wild type, Il1r8-/-, Il18-/-, and Il18-/-/Il1r8-/- mice.
(b) Peripheral CD27low NK cell frequency in wild-type, Il1r8-/-, Il1r1-/- and Il1r8-/-Il1r1-/- mice (left) and IFNγ production by splenic NK cells after IL-12 and IL-1β or IL-18 stimulation (right).
(c, d) Splenic CD27low NK cell frequency in Il1r8+/+ and Il1r8-/- mice upon commensal flora depletion (c) and breeding in co-housing conditions (d).
(e) STED microscopy of human NK cells stimulated with IL-18. Magnification bar: 2μm.
(a-d) *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 between selected relevant comparisons, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test; Centre values and error bars represent mean ± SEM. a, n= 3, 5, or 6 mice; at least 5 animals per group were used (b-d). a-d: one experiment was performed. e: representative images out of three collected from two donors.