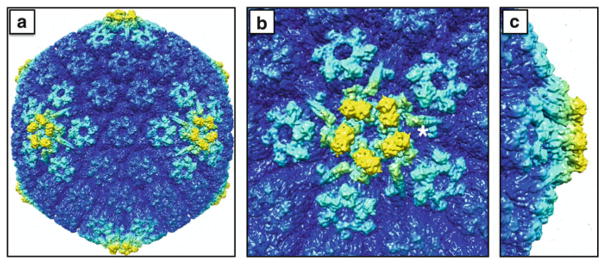
Fig. 8.2.
The outer capsid surface within an extracellular viral particle. The cryoEM density maps are colored to highlight structures that are elevated from the capsid surface: (a) full capsid; (b) top down view of a vertex; (c) side view of a vertex. The pentonal vertices and surrounding peripentonal hexons of the capsid (light cyan) are composed of the major capsid protein (VP5) and, in the case of the hexons, the hexon tip protein (VP26). The elongated structures radiating outward from the penton (one of which is marked with an adjacent asterisk) are composed of two minor capsid proteins, pUL17 and pUL25, and serve as binding sites for the large tegument protein, VP1/2, which also likely contributes to this density. Five copies of a globular structure (yellow) are interdigitated above the VP5 subunits in the underlying penton, and have been proposed to be either an additional portion of the VP1/2 tegument protein or the globular domain of the pUL25 minor capsid protein (see text). In addition to being the most elevated aspects of the capsid surface, the densities highlighted in yellow are absent from nascent capsids assembled in infected cell nuclei. The images were produced using the Chimera software package and EMD-6387