Figure 3.
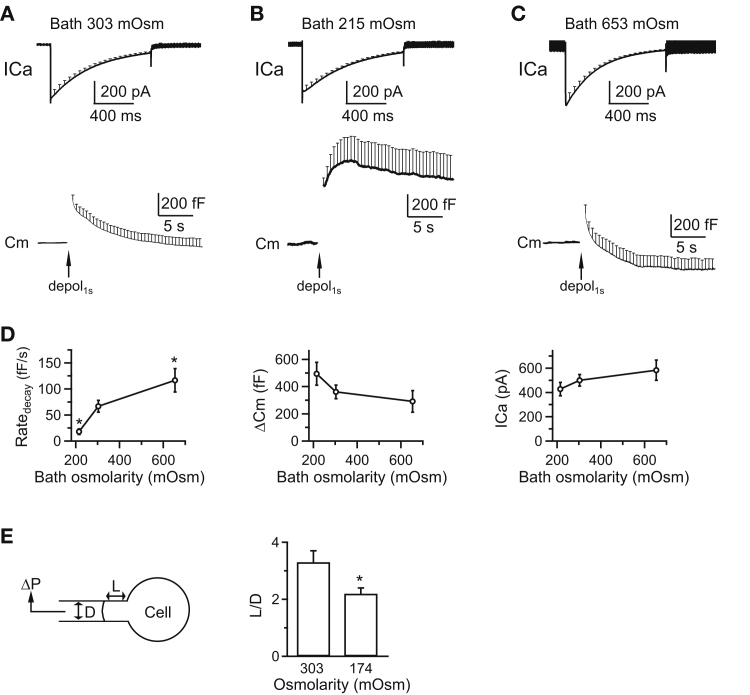
Varying the bath solution osmolarity changes the rate of rapid endocytosis and the membrane tension at chromaffin cells. (A) Shown here is the averaged ICa and capacitance (Cm, mean + SE) induced by depol1s (arrow) from bovine chromaffin cells (20 cells, three bovines) with a control bath solution (mean: 303 mOsm). Mean + SE is plotted every 50 ms in the ICa trace, but every 0.5 s in the Cm trace. (B) Shown here is the averaged ICa and Cm (mean + SE) induced by depol1s (arrow) from chromaffin cells (nine cells, three bovines) with a bath solution at lower osmolarity (mean: 215 mOsm). (C) Given here is the averaged ICa and Cm (mean + SE) induced by depol1s (arrow) from chromaffin cells (14 cells, three bovines) with a bath solution at higher osmolarity (mean: 653 mOsm). (D) Shown here is the Ratedecay, ΔCm, and calcium current charge (QICa) induced by depol1s in bovine chromaffin cells with a mean bath osmolarity of 303 mOsm (control, 20 cells for Ratedecay measurements), 215 mOsm (nine cells for Ratedecay measurements), or 653 mOsm (14 cells for Ratedecay measurements). ∗p < 0.05 (t-test in comparison with control group). (E) Decreasing the bath solution osmolarity increased membrane tension. (Left) Given here are drawings of micropipette aspiration technique. A negative pressure (ΔP) on the pipette (with a diameter D) draws the cell membrane into the pipette by a length L. (Right) Given here is a normalized projection length (L/D, mean + SE) for aspirated cells in a bath solution with a mean osmolarity of 303 mOsm (control, n = 10 cells for L/D measurements) or 174 mOsm (n = 9 cells for L/D measurements; ∗p < 0.05; unpaired two-tailed student’s t-test). ΔP = 1500 Pa.