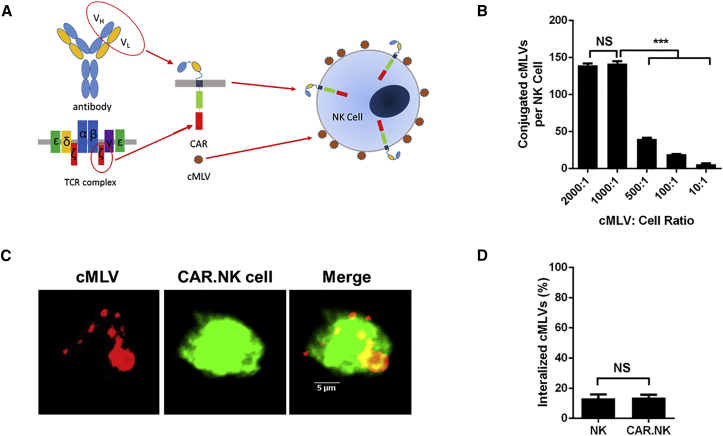
Figure 1.
NK92 Cell Conjugation to Maleimide-Functionalized cMLVs
(A) Schematic of CAR.NK cells conjugated to PTX-loaded cMLVs. CARs are derived from the single-chain variable fragment (scFv) of an antibody and the T cell receptor signaling complex. CARs can be transduced into NK92 cells, and cMLVs can conjugate to the cell surface by interacting with free thiols. (B) cMLVs conjugated to the NK cell surface at various cMLV:cell ratios. cMLVs containing the fluorescent dye DiD were coincubated with NK cells over a range of ratios. The number of cMLVs on the surface of each cell was calculated by analyzing the DiD fluorescence. The ratio of 1,000:1 provided the maximum amount of cMLVs per cell and was used in future experiments. (C) Confocal microscopy of CAR.NK cells conjugated to DiD-loaded cMLVs [cMLV(DiD)]. CAR.NK cells were labeled with 1 μM CFSE and washed with PBS prior to conjugation to cMLV(DiD). Confocal microscopy was used to visualize the cMLVs on the CAR.NK cell surface. Scale bars, 5 μm. (D) Internalization assay of conjugated cMLVs. CAR.NK cells were conjugated with carboxyfluorescein-tagged maleimide-labeled cMLVs. The extracellular conjugation was quenched by trypan blue to differentiate surface-bound and internalized cMLVs 2 hr after conjugation. Attachment of cMLVs to CAR.NK cells did not trigger the internalization of particles by the cells. Summarized statistics are displayed in the graphs (n = 3, mean ± SEM; ***p < 0.001). NS, not significant.