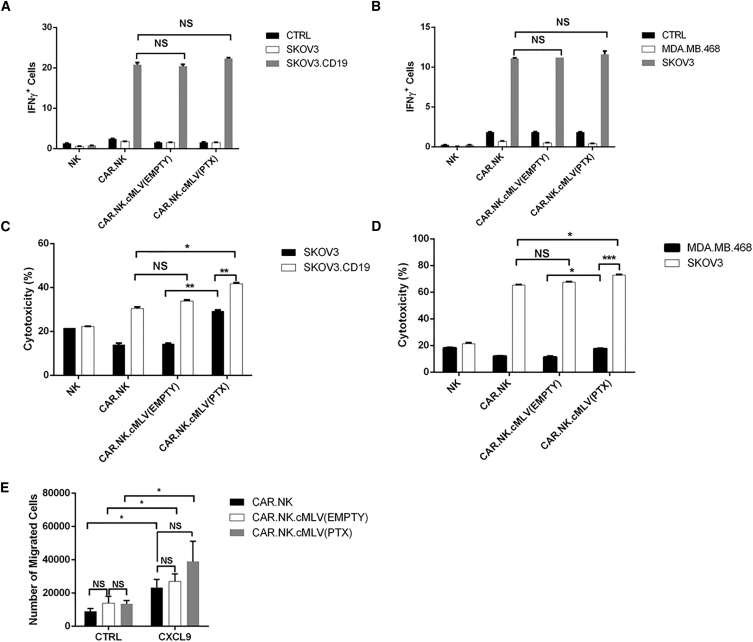
Figure 3.
CAR.NK Cytokine Release and Migration When Conjugated to cMLVs
(A and B) IFN-γ staining assays. Anti-CD19 (A) or anti-Her2 (B) CAR.NK cells were cocultured with various target cells with brefeldin A protein transport inhibitor for 6 hr to detect IFN-γ release. Unstimulated CAR.NK cells served as a negative control. CAR.NK cells were either unconjugated or conjugated with empty cMLVs [CAR.NK.cMLV(EMPTY)] or PTX-loaded cMLVs [CAR.NK.cMLV(PTX)]. IFN-γ was measured with intracellular staining. (C and D) Cytotoxicity assays. Anti-CD19 (C) or anti-Her2 (D) CAR.NK cells were cocultured with various target cells at a 1:1 ratio for 24 hr, and cytotoxicity was measured. CAR.NK cells were either unconjugated or conjugated with empty cMLVs [CAR.NK.cMLV(EMPTY)] or PTX-loaded cMLVs [CAR.NK.cMLV(PTX)]. (E) Migration assay. Unconjugated NK or NK conjugated to cMLV(EMPTY) or cMLV(PTX) were plated in the upper chambers of a Transwell plate. Negative controls had plain media in the lower wells, and CXCL9 was used as a chemoattractant in the lower wells of non-control groups. After 6 hr of incubation, media from the lower chambers were collected and NK cells were counted. Summarized statistics are displayed in the graphs (n = 3; mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). NS, not significant.