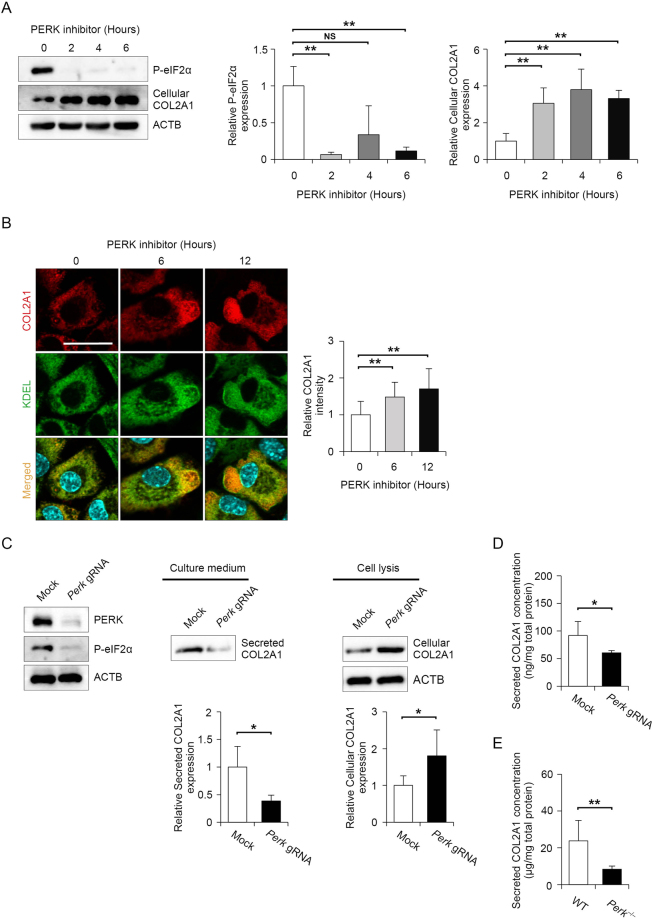
Figure 2.
Type 2 A collagen (COL2A1) secretion was diminished by PERK inhibition, whereas intercellular COL2A1 expression was increased. (A) Representative immunoblots of phosphorylated eIF2α, cellular COL2A1 and ACTB in mouse primary chondrocyte treated with 2 μM PERK inhibitor for the indicated times. The protein levels were normalised to those of ACTB. Data are presented as the mean fold change ± SD compared to that in untreated cells (n = 4 technical replicates, **P < 0.01, NS = not significant). (B) Representative images of immunostaining for COL2A1 and KDEL (ER localization marker) in mouse primary chondrocytes treated with 2 μM PERK inhibitor for the indicated times. Relative fluorescence intensity was quantified in comparison to that of untreated cells and each group data consisted of images of 10 cells (n = 10 technical replicates, *P < 0.05). Scale bar, 200 μm. (C) Representative immunoblots of PERK, ACTB, phosphorylated eIF2α and secreted and cellular COL2A1 in collagen-secreting rat chondrosarcoma (RCS) cells stably expressing Cas9 and mock gRNA or three Perk-specific gRNAs. Data are presented as the mean fold change ± SD compared to that in mock gRNA-expressing cells (n = 4 technical replicates, **P < 0.01). (D) Quantitative assessment of secreted COL2A1 in collagen-secreting RCS cells stably expressing Cas9 and mock gRNA or three Perk-specific gRNAs. Values were normalised by the total protein amount of the cells and shown as the mean ± SD (n = 4 technical replicates, *P < 0.05). (E) Quantitative assessment of secreted COL2A1 in primary chondrocytes derived from wild-type or Perk−/− mice at 18.5 days postcoitum (dpc). Values were normalised by the total protein amount of the cells and shown as the mean ± SD (n = 5 technical replicates, *P < 0.05).