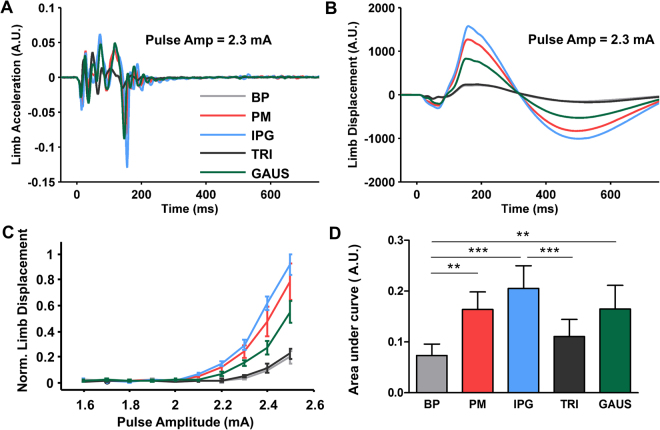
Figure 2.
Motor cortex stimulation with different pulse-shapes (Exp. 1, Phase I). (A) Shows the bandpass filtered, averaged (5 repetitions), limb acceleration data for the five different pulse-shapes tested at one amplitude. (B) Shows the limb displacement data calculated from the acceleration data in panel A. (C) Shows the effect of pulse-shape on normalized limb displacement, calculated from the peak in panel B, for a range of pulse amplitudes in one animal. In this rat, biphasic (BP) and triangular (TRI) pulse-shapes produce relatively small limb displacements while Gaussian (GAUS), pseudomonophasic (PM) and interphase gap (IPG) pulse-shapes produce progressively larger displacements for an equivalent pulse amplitude. (D) These findings are reflected in the data at the group level (n = 6). Data are shown as means ± SD. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.